
An n-type and p-type silicon can be obtained by doping pure silicon with:
A. Arsenic and Phosphorus
B. Indium and Aluminium
C. Phosphorus and Indium
D. Aluminium and Boron
Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint: Recall that the majority charge carriers in the n and p-type semiconductors are electrons and holes, and are doped with pentavalent and trivalent atoms respectively. In such a case, determine which of the options are a combination of pentavalent and trivalent atoms respectively. The atom with five valence electrons donates one electron to the crystal as a charge carrier, whereas the atom with three valence electrons accepts one electron from the crystal, creating electron holes as charge carriers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what doping is.
It is the process by which the conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor (pure form) is modulated at the structural level by an intentional introduction of impurities into the semiconducting crystal lattice. This either generates a surplus or a deficiency in valence electrons and ultimately provides free charge carriers (electrons or electron holes) to the semiconductor.
When pure silicon is doped with impurities (which we call dopants), the resulting semiconductor is called an extrinsic semiconductor, and they are of two types.
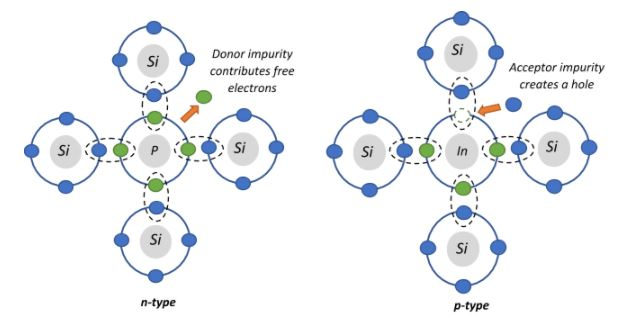
1. n-type semiconductors:
These are formed by doping the silicon with electron donor atoms. The dopant is usually a pentavalent atom which has five valence electrons, four of which form covalent bonds with the neighbouring silicon atoms as shown in the figure, since silicon is a tetravalent element. The remaining one valence electron is not bound to any lattice silicon atom and acts as a free charge carrier which adds to the conductivity of the conductor. The n in the n-type stands for the negative electrons, which are the majority charge carriers in the crystal.
From the options given to us, the two pentavalent atoms are Arsenic and Phosphorus.
2. p-type semiconductors:
These are formed by doping the silicon with electron acceptor atoms. The dopant is usually a trivalent atom which has three valence electrons, all of which form covalent bonds with the neighbouring silicon atoms. Now, there is a lack of one electron (which we call a hole) for silicon to complete its tetravalent bond. This vacant state gets occupied by an external electron, which in turn leaves a hole at its place and this way the holes bring out conduction. The p in the p-type stands for the positive charge of the hole, which are the majority charge carriers in the crystal.
From the options given to us, the trivalent atoms are Boron, Aluminium and Indium.
Thus, putting together the correct combination of the n and p-type semiconductors, the correct choice would be C. Phosphorus and Indium.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that in the band structure of the n and p-type semiconductors the electrons in the conduction band are the majority charge carriers whereas the holes in the valence band are the majority charge carriers respectively. In the n-type semiconductors, the fermi level lies closer to the conduction band and in the p-type, the fermi level is below the intrinsic fermi level and is closer to the valence band.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what doping is.
It is the process by which the conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor (pure form) is modulated at the structural level by an intentional introduction of impurities into the semiconducting crystal lattice. This either generates a surplus or a deficiency in valence electrons and ultimately provides free charge carriers (electrons or electron holes) to the semiconductor.
When pure silicon is doped with impurities (which we call dopants), the resulting semiconductor is called an extrinsic semiconductor, and they are of two types.

1. n-type semiconductors:
These are formed by doping the silicon with electron donor atoms. The dopant is usually a pentavalent atom which has five valence electrons, four of which form covalent bonds with the neighbouring silicon atoms as shown in the figure, since silicon is a tetravalent element. The remaining one valence electron is not bound to any lattice silicon atom and acts as a free charge carrier which adds to the conductivity of the conductor. The n in the n-type stands for the negative electrons, which are the majority charge carriers in the crystal.
From the options given to us, the two pentavalent atoms are Arsenic and Phosphorus.
2. p-type semiconductors:
These are formed by doping the silicon with electron acceptor atoms. The dopant is usually a trivalent atom which has three valence electrons, all of which form covalent bonds with the neighbouring silicon atoms. Now, there is a lack of one electron (which we call a hole) for silicon to complete its tetravalent bond. This vacant state gets occupied by an external electron, which in turn leaves a hole at its place and this way the holes bring out conduction. The p in the p-type stands for the positive charge of the hole, which are the majority charge carriers in the crystal.
From the options given to us, the trivalent atoms are Boron, Aluminium and Indium.
Thus, putting together the correct combination of the n and p-type semiconductors, the correct choice would be C. Phosphorus and Indium.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Remember that in the band structure of the n and p-type semiconductors the electrons in the conduction band are the majority charge carriers whereas the holes in the valence band are the majority charge carriers respectively. In the n-type semiconductors, the fermi level lies closer to the conduction band and in the p-type, the fermi level is below the intrinsic fermi level and is closer to the valence band.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




