
An object AB is kept in front of a concave mirror as shown in the figure.
(i) Complete the ray diagram showing the image formation of the object.
(ii) How will the position and intensity of the image be affected if the lower half of the mirror’s reflecting surface is painted black?
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: Draw three rays from the point A, one parallel to the principal axis, second passing through the focus and third passing through the centre. We know that after reflection, light ray, parallel to the principal axis through the focus and the rays passing through the focus becomes parallel. A ray passing through the centre retraces its path. The point where the three rays meet is the position of the image. Intensity of light depends on the number of light rays forming the image.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) The relation between the position of the object and position of its image from the pole of the mirror is given by the equation $\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ …….(i).
f is the focal length of the mirror. For a concave mirror, the value of focal length is negative. For a convex mirror, the value of focal length is positive.
Draw a ray parallel to the principal axis from the tip (A) of the object. When a ray of light parallel to the principal axis, it passes through the focus (point F) of a concave mirror, after reflection.
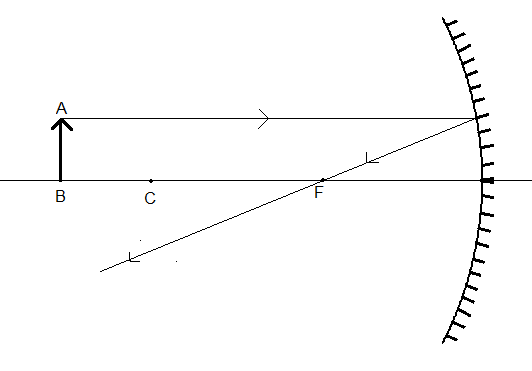
Now, draw one more ray from point A passing through the focus (F) of the mirror. It is converse to the above paragraph. When a ray of light passing through the focus of a concave falls on the mirror, after reflection it travels parallel to the principal axis.
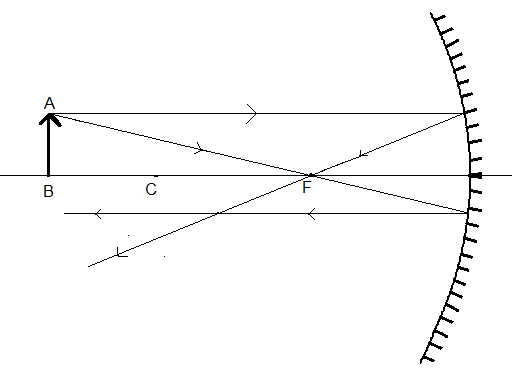
Draw a third ray from point A passing through the centre (C) of the concave mirror. When a ray of light passing through the centre of a concave mirror falls a on the mirror, after reflection it retraces its path i.e. It again passes through the centre (C) of the concave mirror.
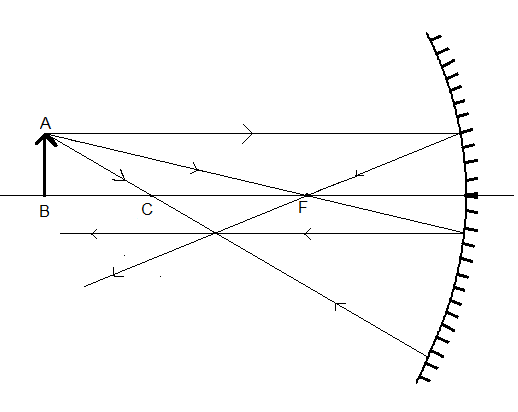
All the three rays will meet a point. The point where all the rays will meet will be the tip of the image A’.
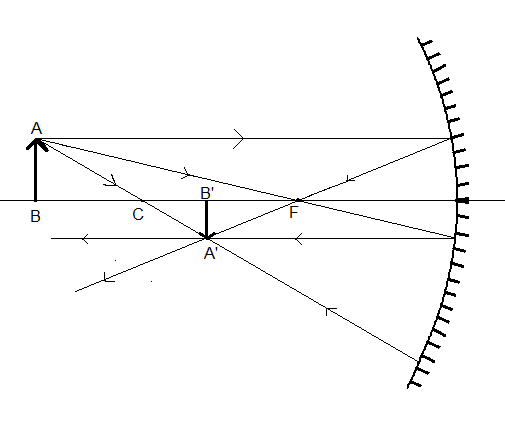
Therefore, we found the position and size of the image.
(ii) If the lower part of the mirror is painted black, the position of the image will not change because the position of the image depends on the position of the object and the focal length of the mirror as you can see in equation (i). It is independent of the size of the mirror.
However, the intensity of the image will be affected. Intensity of an image depends on the number of light rays making that image. More the number of rays, more is the intensity of the image and vice-versa. Therefore, if we consider only half of the given mirror, the intensity of the image will be reduced to half.
Note: It is to be noted that the values of positions of the object and its image depend on a sign convection.
(i) The distances are measured from the pole.
(ii) Distances measured in the direction of incident rays are taken as positive while in the direction opposite of incident rays are taken negative.
(iii) Distances above the principal axis are taken positive and below the principal axis are taken negative.
Complete step by step answer:
(i) The relation between the position of the object and position of its image from the pole of the mirror is given by the equation $\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$ …….(i).
f is the focal length of the mirror. For a concave mirror, the value of focal length is negative. For a convex mirror, the value of focal length is positive.
Draw a ray parallel to the principal axis from the tip (A) of the object. When a ray of light parallel to the principal axis, it passes through the focus (point F) of a concave mirror, after reflection.

Now, draw one more ray from point A passing through the focus (F) of the mirror. It is converse to the above paragraph. When a ray of light passing through the focus of a concave falls on the mirror, after reflection it travels parallel to the principal axis.

Draw a third ray from point A passing through the centre (C) of the concave mirror. When a ray of light passing through the centre of a concave mirror falls a on the mirror, after reflection it retraces its path i.e. It again passes through the centre (C) of the concave mirror.

All the three rays will meet a point. The point where all the rays will meet will be the tip of the image A’.

Therefore, we found the position and size of the image.
(ii) If the lower part of the mirror is painted black, the position of the image will not change because the position of the image depends on the position of the object and the focal length of the mirror as you can see in equation (i). It is independent of the size of the mirror.
However, the intensity of the image will be affected. Intensity of an image depends on the number of light rays making that image. More the number of rays, more is the intensity of the image and vice-versa. Therefore, if we consider only half of the given mirror, the intensity of the image will be reduced to half.
Note: It is to be noted that the values of positions of the object and its image depend on a sign convection.
(i) The distances are measured from the pole.
(ii) Distances measured in the direction of incident rays are taken as positive while in the direction opposite of incident rays are taken negative.
(iii) Distances above the principal axis are taken positive and below the principal axis are taken negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




