
An object is placed at a distance of 10cm from a convex lens of focal length 20cm. Find the position and nature of image.
Answer
524.2k+ views
Hint: In such questions, first of all we’re supposed to draw the diagram of the lens to correctly analyze the scenario. To draw the diagram, we draw the object of sufficient length and then with the use of two rays, one from the top and other from the bottom, we trace the image of the object. We do it following the basic rules of tracing like rays parallel to the principal axis will cut the principle axis on the focus and rays passing through the optical centre goes undeflected.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u}-\dfrac{1}{v}$, called the lens formula where ‘u’ is the object distance and ‘v’ is the image distance measured from the pole of the lens of focal length ‘f’.
Complete step by step answer:
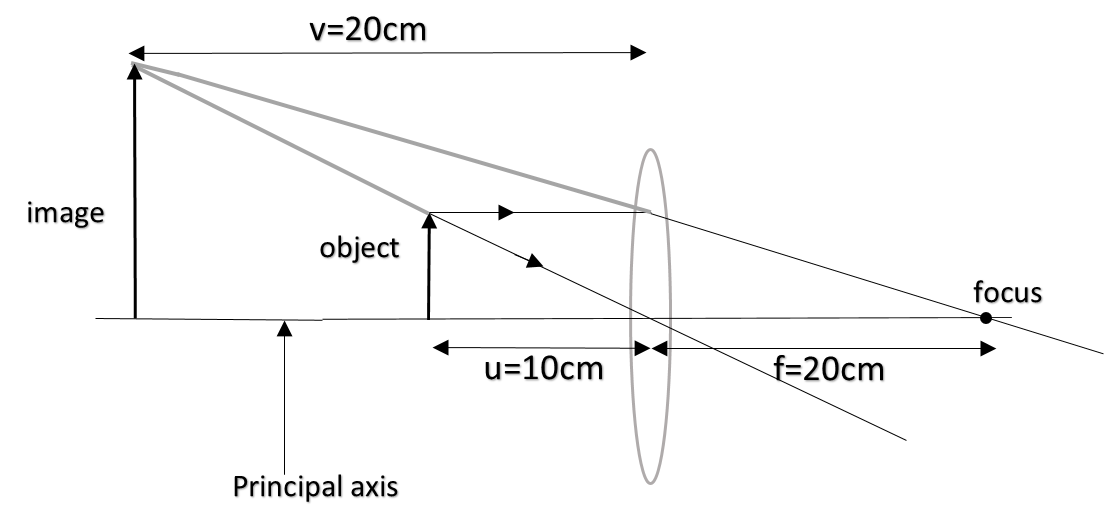
u=-10cm [as object is always placed before the lens, so negative sign]
and f=+20cm [as focal length of convex lens is positive]
hence, using lens formula: $\dfrac{1}f{} = \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Putting the given values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-10}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{10}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{10} = -\dfrac{1}{20}$
$\therefore $ v=-20cm
Hence the image will be formed on the left side of the lens (shown by negative sign) at a distance of 20 cm.
Also we can see that the object is in between the lens and image, hence the image is virtual. As both the object and image is above the principle axis, hence it is erect too.
Note:
Hence we see that the image is virtual and erect. Also by diagram we can see that the image is larger than the object and hence is magnified. But it’s not a good way to see the size. Best way is to check for the magnification which is the ratio of image and object distance.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{u}-\dfrac{1}{v}$, called the lens formula where ‘u’ is the object distance and ‘v’ is the image distance measured from the pole of the lens of focal length ‘f’.
Complete step by step answer:

u=-10cm [as object is always placed before the lens, so negative sign]
and f=+20cm [as focal length of convex lens is positive]
hence, using lens formula: $\dfrac{1}f{} = \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}$
Putting the given values, we get
$\dfrac{1}{20}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{-10}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{10}$
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{20}-\dfrac{1}{10} = -\dfrac{1}{20}$
$\therefore $ v=-20cm
Hence the image will be formed on the left side of the lens (shown by negative sign) at a distance of 20 cm.
Also we can see that the object is in between the lens and image, hence the image is virtual. As both the object and image is above the principle axis, hence it is erect too.
Note:
Hence we see that the image is virtual and erect. Also by diagram we can see that the image is larger than the object and hence is magnified. But it’s not a good way to see the size. Best way is to check for the magnification which is the ratio of image and object distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




