
An orthotropous ovule is one, in which micropyle and chalaza are
(a) In the straight line of a funiculus
(b) Parallel to the funiculus
(c) At right angles to the funiculus
(d) Oblique to the funiculus
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: The ovule in angiosperms is attached to the placenta by a slender stalk called the funicle or funiculus. It is responsible for the orientation in which the ovule is found attached to the placenta.
Complete answer:
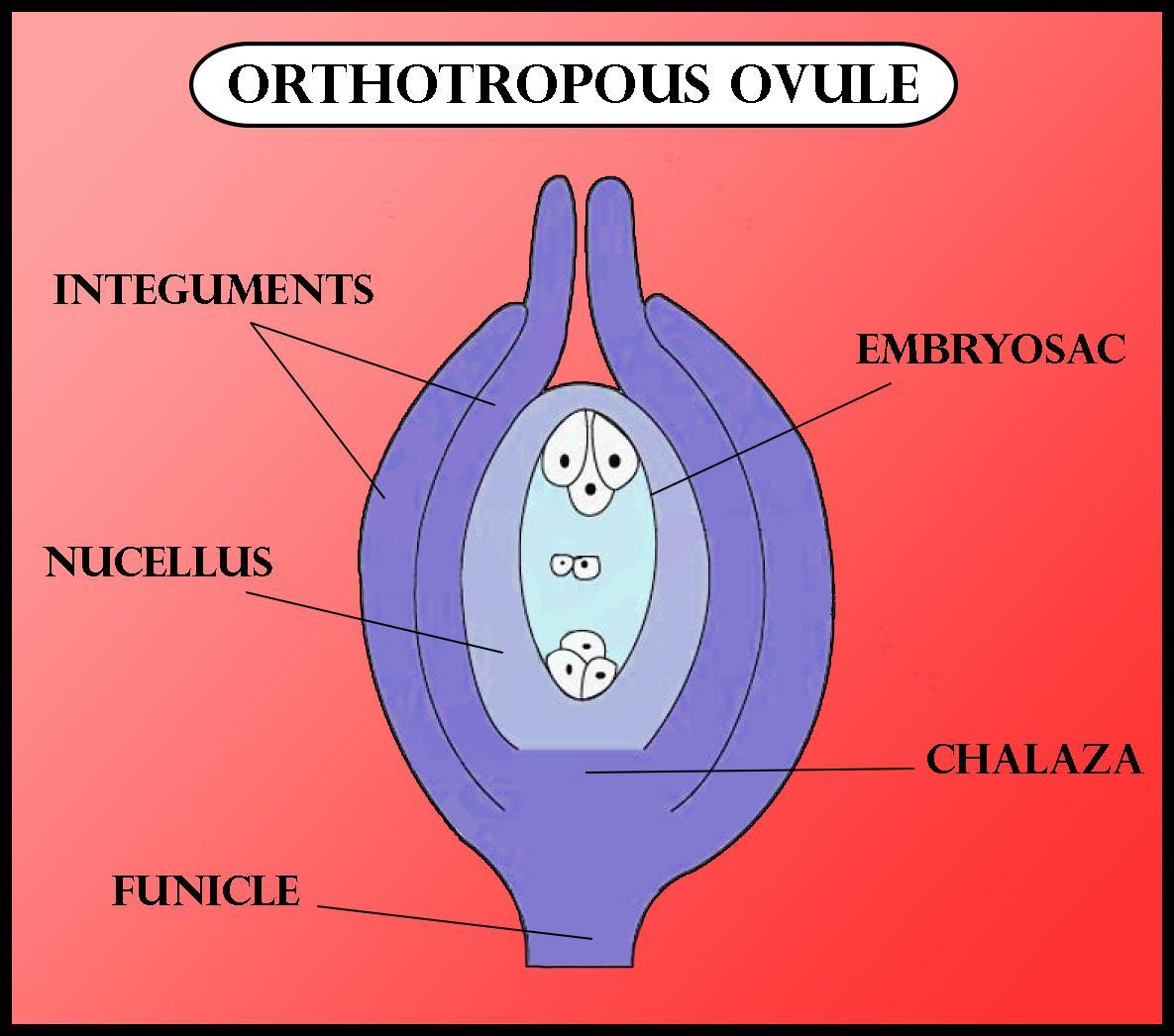
An orthotropous ovule has the micropyle and chalaza in a straight line of the funiculus. Such type of ovule is also known as straight or erect ovule. It is also known as anatropous ovule. Orthotropous ovules have evolved independently in the various groups of angiosperms.
- The placenta is a ridge of parenchymatous tissue in the inner wall of the ovary to which ovules are attached.
- How the placenta is distributed in the cavity of an ovary is called placentation.
- The point of attachment of the ovule to its stalk or funicle is known as hilum.
- The ovule contains a thin-walled parenchymatous cell called nucellus.
- The nucellus is protected by one or two multicellular coating called integuments.
- The basal portion of the nucellus from where the integuments emerge is called chalaza.
- A small opening at the apex of the integuments is known as micropyle.
- The micropylar end acts as an entry pathway for the pollen tube to transfer the male gametophyte. The embryo sac is embedded in the micropylar region.
- The other curved ovules are anatropous, campylotropous, amphitropous, and circinotropous.
So, the correct answer is, ‘In the straight line of funiculus.’
Note: Orthotropous ovule is the simplest and very primitive type of ovule. Micropyle, funicle, and chalaza lie in one vertical plane. Examples of plants having orthotropous ovules are, Piper nigrum, Polygonum, Piper betel, and all gymnosperms.
Complete answer:
An orthotropous ovule has the micropyle and chalaza in a straight line of the funiculus. Such type of ovule is also known as straight or erect ovule. It is also known as anatropous ovule. Orthotropous ovules have evolved independently in the various groups of angiosperms.
- The placenta is a ridge of parenchymatous tissue in the inner wall of the ovary to which ovules are attached.
- How the placenta is distributed in the cavity of an ovary is called placentation.
- The point of attachment of the ovule to its stalk or funicle is known as hilum.
- The ovule contains a thin-walled parenchymatous cell called nucellus.
- The nucellus is protected by one or two multicellular coating called integuments.
- The basal portion of the nucellus from where the integuments emerge is called chalaza.
- A small opening at the apex of the integuments is known as micropyle.
- The micropylar end acts as an entry pathway for the pollen tube to transfer the male gametophyte. The embryo sac is embedded in the micropylar region.
- The other curved ovules are anatropous, campylotropous, amphitropous, and circinotropous.

So, the correct answer is, ‘In the straight line of funiculus.’
Note: Orthotropous ovule is the simplest and very primitive type of ovule. Micropyle, funicle, and chalaza lie in one vertical plane. Examples of plants having orthotropous ovules are, Piper nigrum, Polygonum, Piper betel, and all gymnosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




