
An ovule which becomes curved so that the nucellus and the embryo sac lie at the right angle to the funicle is ....
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: In seed plants, the female reproductive organ is Ovule. It is a place where a seed actually develops after fertilization, this forms the seed of a flowering plant. The arrangement of parts of Ovary helps in fertilization procedures.
Complete answer:
The ovule is referred to as Megasporangium. Ovule is made up of parenchymatous tissue, nucellus, the integuments, Integuments is the outer protective layer of the ovule, this forms the outermost layer and inner most layer (Embryo sac). They are attached to the placentae on the inner wall of the ovary by means of Stalk called as Funicle. The mature ovule shows a small opening called Micropyle and opposite to that is chalaza.
Hemi anatropous:
Hemi anatropus is a type, where the ovule becomes curved so that the nucellus and embryo sac lie at right angles to the funicle. This is also referred to as hemitropous. In most of the Angiosperms, anatropous ovule is present, it looks like the ovule is twisted, so the Micropyle lies close to the funicle.
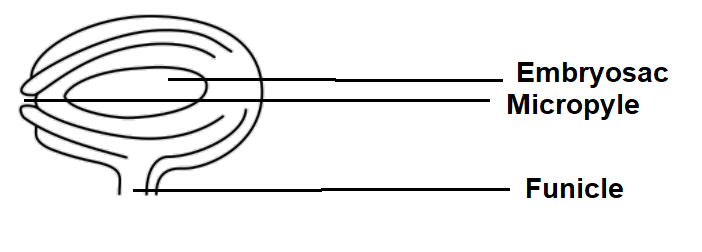
Example: Hemi anatropous type of ovule is found in Ranunculus.
Note:
There are different types of ovules based on their shapes. After fertilization the ovule starts to swell and becomes tight to become a seed, while the ovary starts to grow and becomes a fruit.
The important components of the ovule are, Nucellus is the largest part of the ovule, this contains an Embryo sac and nutritive tissue. This is seen in flowering plants. Integument is the outer protective layer of the ovule (unitegmic is one integument in the ovule). Female gametophyte is part of ovules that contains the gamete producing sex organs.
Complete answer:
The ovule is referred to as Megasporangium. Ovule is made up of parenchymatous tissue, nucellus, the integuments, Integuments is the outer protective layer of the ovule, this forms the outermost layer and inner most layer (Embryo sac). They are attached to the placentae on the inner wall of the ovary by means of Stalk called as Funicle. The mature ovule shows a small opening called Micropyle and opposite to that is chalaza.
Hemi anatropous:
Hemi anatropus is a type, where the ovule becomes curved so that the nucellus and embryo sac lie at right angles to the funicle. This is also referred to as hemitropous. In most of the Angiosperms, anatropous ovule is present, it looks like the ovule is twisted, so the Micropyle lies close to the funicle.

Example: Hemi anatropous type of ovule is found in Ranunculus.
Note:
There are different types of ovules based on their shapes. After fertilization the ovule starts to swell and becomes tight to become a seed, while the ovary starts to grow and becomes a fruit.
The important components of the ovule are, Nucellus is the largest part of the ovule, this contains an Embryo sac and nutritive tissue. This is seen in flowering plants. Integument is the outer protective layer of the ovule (unitegmic is one integument in the ovule). Female gametophyte is part of ovules that contains the gamete producing sex organs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




