
What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray when an ordinary ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at polarizing angle?
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint The angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray is always \[90^\circ \] , when a ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at polarizing angle. This can be derived from Brewster’s law.
Complete step-by-step solution:
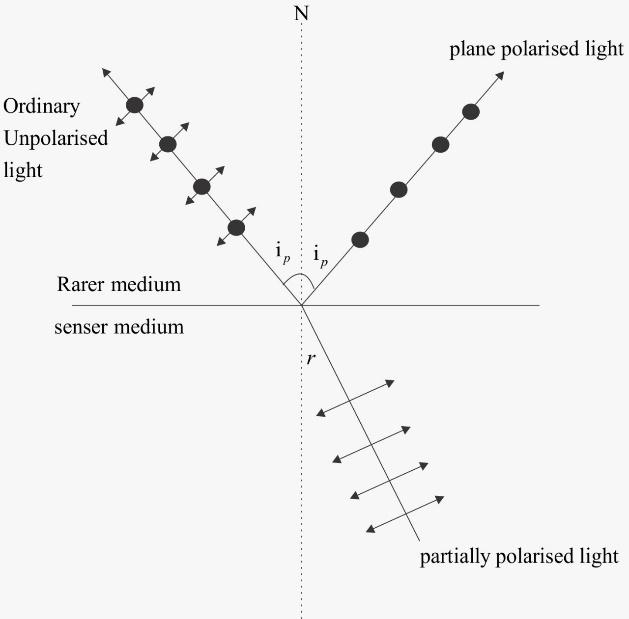
The angle of incidence at which a fully plane polarised light is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection is known as the polarizing angle (also called Brewster's angle).
We can better understand the polarizing angle with the help of Brewster's Law which states that when an ordinary unpolarised light is incident at an angle of polarization $\left( {{i_p}} \right)$ on the boundary separating air from a medium of refractive index $\mu $ , then reflected light becomes fully polarized and the tangent of the angle of polarization is numerically equal to the refractive index of the medium i.e. $\mu = \tan {i_p}$ ….(i)
Now, from Snell’s law we can say that $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {i_p}}}{{\sin r}}$ …..(ii) where r is the angle of refraction in denser medium.
Now, from equations (i) and (ii), we have
$\tan {i_p} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_p}}}{{\sin r}}$
On further solving we have
$\cos {i_p} = \sin r$
Now as we know, $\cos \theta = \sin \left( {90^\circ - \theta } \right)$
So, $\sin \left( {90^\circ - {i_p}} \right) = \sin r$
On simplification we have
${i_p} + r = 90^\circ $
Now, as clear from the diagram that if ${i_p} + r = 90^\circ $ then the angle between reflected ray and refracted ray will be $180^\circ - 90^\circ = 90^\circ $ .
Hence, when a ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at polarizing angle then the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray is \[90^\circ \] .
Note:Snell’s law is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given color and for the given pair of media.
Brewster’s window is an application of Brewster's law and Brewster's angle. It is a window made up of glass which transmits 100% of light. These windows are used in gas lasers and in solid state lasers.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The angle of incidence at which a fully plane polarised light is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection is known as the polarizing angle (also called Brewster's angle).
We can better understand the polarizing angle with the help of Brewster's Law which states that when an ordinary unpolarised light is incident at an angle of polarization $\left( {{i_p}} \right)$ on the boundary separating air from a medium of refractive index $\mu $ , then reflected light becomes fully polarized and the tangent of the angle of polarization is numerically equal to the refractive index of the medium i.e. $\mu = \tan {i_p}$ ….(i)
Now, from Snell’s law we can say that $\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {i_p}}}{{\sin r}}$ …..(ii) where r is the angle of refraction in denser medium.

Now, from equations (i) and (ii), we have
$\tan {i_p} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_p}}}{{\sin r}}$
On further solving we have
$\cos {i_p} = \sin r$
Now as we know, $\cos \theta = \sin \left( {90^\circ - \theta } \right)$
So, $\sin \left( {90^\circ - {i_p}} \right) = \sin r$
On simplification we have
${i_p} + r = 90^\circ $
Now, as clear from the diagram that if ${i_p} + r = 90^\circ $ then the angle between reflected ray and refracted ray will be $180^\circ - 90^\circ = 90^\circ $ .
Hence, when a ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at polarizing angle then the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray is \[90^\circ \] .
Note:Snell’s law is defined as the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given color and for the given pair of media.
Brewster’s window is an application of Brewster's law and Brewster's angle. It is a window made up of glass which transmits 100% of light. These windows are used in gas lasers and in solid state lasers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




