
Aniline doesn’t react with
A. \[{\text{dilute HCl}}\]
B. \[{\text{dilute NaOH}}\]
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: To determine the reactivity of aniline, we need the proper structure of aniline and the concept of nucleophile and electrophile in an organic reaction. We also need to know the reason for the basic nature of aniline.
Complete answer:
The structure of aniline contains an ammonia group \[ + {\text{ dilute HCl}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }\] attached to the benzene ring.
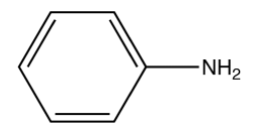
Due to the presence of a lone pair of nitrogen atoms of the ammonia group of the aniline, due to which it acts as a nucleophile. It’s ability to donate the lone pair of electrons to an electrophilic center makes it basic in nature. Now, as the lone pair on the nitrogen atom is in conjugation or is under resonance with the benzene ring, it is not easily available for donation to an electrophile due to which its basic nature decreases. Hence, making aniline a weak base.
Now, we know that aniline is a weak base.
So, when aniline reacts with \[{\text{dilute HCl}}\], \[HCl\] on cleavage during the reaction produces \[{H^ + }\]and \[C{l^ - }\]because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen.
Here, \[C{l^ - }\]has a negative charge on it making it a nucleophile and hence, it won’t react with aniline whereas \[{H^ + }\]having a positive charge will act as an electrophile and hance, can receive the donated lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen atom of aniline.
Therefore, we can say that aniline will react with dilute HCl to produce an anilinium ion and a chloride ion.
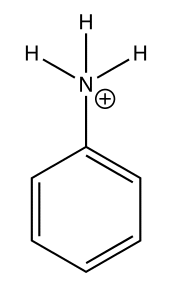
The structure drawn above is of the ANILINIUM ION
Now, when we add dilute \[NaOH\] to aniline, aniline won’t react dilute \[NaOH\] because \[NaOH\] is an ionic compound which produces an hydroxide ion \[(O{H^ - })\] on dissociation in the reaction mixture.
Since, the hydroxide ion has negative charge on it, it will act as a nucleophile and will not react with aniline. Also, the \[N{a^ + }\] ion produced in the reaction is an ion and won’t react with aniline as aniline is a weak base.
So, aniline will not react with A. dilute \[NaOH\].
Note:
While solving this type question, students generally get confused about which species will act as a nucleophile or an electrophile during the reaction and how both of them in a reaction will interact with each other to form a product.
Complete answer:
The structure of aniline contains an ammonia group \[ + {\text{ dilute HCl}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ - }\] attached to the benzene ring.

Due to the presence of a lone pair of nitrogen atoms of the ammonia group of the aniline, due to which it acts as a nucleophile. It’s ability to donate the lone pair of electrons to an electrophilic center makes it basic in nature. Now, as the lone pair on the nitrogen atom is in conjugation or is under resonance with the benzene ring, it is not easily available for donation to an electrophile due to which its basic nature decreases. Hence, making aniline a weak base.
Now, we know that aniline is a weak base.
So, when aniline reacts with \[{\text{dilute HCl}}\], \[HCl\] on cleavage during the reaction produces \[{H^ + }\]and \[C{l^ - }\]because chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen.
Here, \[C{l^ - }\]has a negative charge on it making it a nucleophile and hence, it won’t react with aniline whereas \[{H^ + }\]having a positive charge will act as an electrophile and hance, can receive the donated lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen atom of aniline.
Therefore, we can say that aniline will react with dilute HCl to produce an anilinium ion and a chloride ion.

The structure drawn above is of the ANILINIUM ION
Now, when we add dilute \[NaOH\] to aniline, aniline won’t react dilute \[NaOH\] because \[NaOH\] is an ionic compound which produces an hydroxide ion \[(O{H^ - })\] on dissociation in the reaction mixture.
Since, the hydroxide ion has negative charge on it, it will act as a nucleophile and will not react with aniline. Also, the \[N{a^ + }\] ion produced in the reaction is an ion and won’t react with aniline as aniline is a weak base.
So, aniline will not react with A. dilute \[NaOH\].
Note:
While solving this type question, students generally get confused about which species will act as a nucleophile or an electrophile during the reaction and how both of them in a reaction will interact with each other to form a product.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




