
Application of a forward bias to a p-n junction:
A. Increases the number of donors on the n-side.
B. Increases the electric field in the depletion zone.
C. Increases the potential difference across the depletion zone.
D. Widens the depletion zone.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: p-n junction is an active element of the circuit, which is used where we want the flow of current in one direction and not in both. It is called a p-n junction because it is built using a p-type and a n-type semiconductor. When this diode is forward biased, only in that case it allows the current to flow through it.
Complete answer:
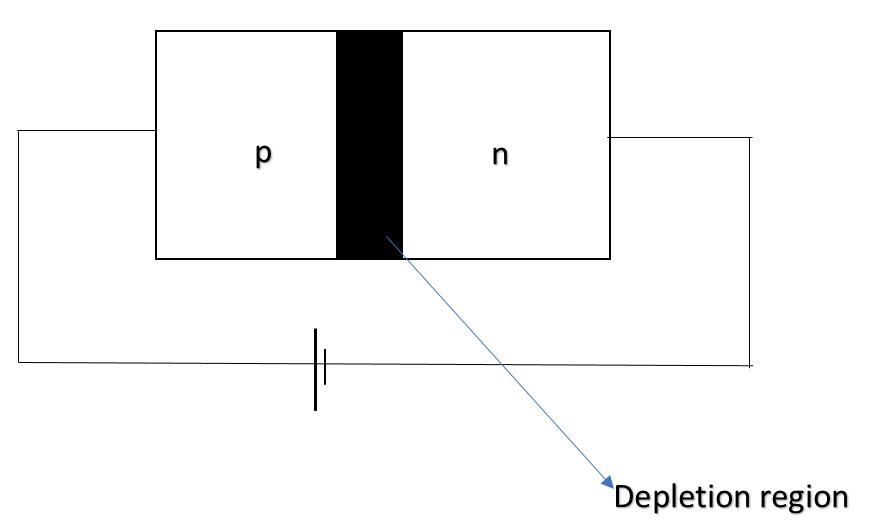
The above diagram shows a forward biased p-n junction. We can identify the forward or reverse bias of a p-n junction by knowing its connection with the battery. If the positive terminal of the battery is connected with p type semiconductor and negative terminal to the n type semiconductor, then the p-n junction will be forward biased and otherwise it is reverse biased and no current will flow through it in that case.
Now, in the forward biased condition, the negative terminal of the battery pushes the electrons in the n type region. The holes present in the depletion region hence get filled up and the width of depletion region reduces. This means that the concentration of electrons on the n side of the junction gets increased thereby reducing the width of the depletion region.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Depletion region is the region of meeting of p and n type material. In forward biased conditions, its width is minimal. Hence it allows the passage of electrons very easily. One must also note that all other options are very true, but for reverse biased conditions. In short we can say the battery pushes more electrons (donors) into the n-type material side.
Complete answer:

The above diagram shows a forward biased p-n junction. We can identify the forward or reverse bias of a p-n junction by knowing its connection with the battery. If the positive terminal of the battery is connected with p type semiconductor and negative terminal to the n type semiconductor, then the p-n junction will be forward biased and otherwise it is reverse biased and no current will flow through it in that case.
Now, in the forward biased condition, the negative terminal of the battery pushes the electrons in the n type region. The holes present in the depletion region hence get filled up and the width of depletion region reduces. This means that the concentration of electrons on the n side of the junction gets increased thereby reducing the width of the depletion region.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
Depletion region is the region of meeting of p and n type material. In forward biased conditions, its width is minimal. Hence it allows the passage of electrons very easily. One must also note that all other options are very true, but for reverse biased conditions. In short we can say the battery pushes more electrons (donors) into the n-type material side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




