
Why are certain compounds called hydrocarbons? Write the general formula for homologous series of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes and also draw the structure of the first member of each series. Write the name of the reaction that converts alkenes into alkanes and also write a chemical equation to show necessary conditions for the reaction to occur.
Answer
522.8k+ views
Hint: Homologous series of compounds is referred to as the series of compounds that have the same general formula but differ from adjacent members by $-C{H}_{2}-$ group. They are determined by the hydrocarbon chain.
Complete step by step answer:
Certain compounds are called hydrocarbons because they are a group of compounds which are made up of hydrogen and carbon.
The homologous group of compounds are like alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, etc.
The alkanes only have carbon atoms that are attached to the other carbon atoms through single bonds.
In alkenes, the carbon atoms are connected through at least one double bond and the rest might or might not be single bonds.
In alkynes, the carbon atoms are connected through at least one triple bond and the rest might or might not be single bonds.
The homologous group of compounds have the same general formula.
The general formula of homologous series alkanes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n+2}$.
The general formula of homologous series alkenes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n}$.
The general formula of homologous series alkynes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n-2}$.
The first member of alkanes homologous series is methane.
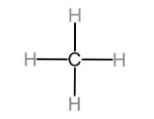
The first member of alkenes homologous series is ethene.
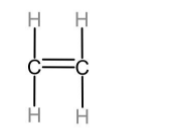
The first member of alkynes homologous series is ethyne.
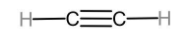
Ethene can be converted to ethane through the reaction known as catalytic hydrogenation reaction. This is known as this because it uses Raney Ni, Pt, or Pd as a catalyst. The reaction is given below.
$\underset { Ethene }{ { C }H_{ 2 }=C{ H }_{ 2 } } \quad +\quad \underset { Hydrogen }{ { H }_{ 2 } } \quad \xrightarrow [ Nickel ]{ 423\quad K } \quad \underset { Ethane }{ { CH }_{ 3 }-C{ H }_{ 3 } }$
The conditions which are necessary for this reaction are the presence of a catalyst Ni and the temperature should be 423K.
Note: The first member of the homologous series of alkene and alkyne have 2 carbon atoms because they involve double and triple bonds respectively which is not possible for a single carbon. Also, if we are using Pt or Pd as a catalyst then the reaction can be carried out at room temperatures.
Complete step by step answer:
Certain compounds are called hydrocarbons because they are a group of compounds which are made up of hydrogen and carbon.
The homologous group of compounds are like alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, etc.
The alkanes only have carbon atoms that are attached to the other carbon atoms through single bonds.
In alkenes, the carbon atoms are connected through at least one double bond and the rest might or might not be single bonds.
In alkynes, the carbon atoms are connected through at least one triple bond and the rest might or might not be single bonds.
The homologous group of compounds have the same general formula.
The general formula of homologous series alkanes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n+2}$.
The general formula of homologous series alkenes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n}$.
The general formula of homologous series alkynes is ${C}_{n}{H}_{2n-2}$.
The first member of alkanes homologous series is methane.

The first member of alkenes homologous series is ethene.

The first member of alkynes homologous series is ethyne.
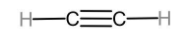
Ethene can be converted to ethane through the reaction known as catalytic hydrogenation reaction. This is known as this because it uses Raney Ni, Pt, or Pd as a catalyst. The reaction is given below.
$\underset { Ethene }{ { C }H_{ 2 }=C{ H }_{ 2 } } \quad +\quad \underset { Hydrogen }{ { H }_{ 2 } } \quad \xrightarrow [ Nickel ]{ 423\quad K } \quad \underset { Ethane }{ { CH }_{ 3 }-C{ H }_{ 3 } }$
The conditions which are necessary for this reaction are the presence of a catalyst Ni and the temperature should be 423K.
Note: The first member of the homologous series of alkene and alkyne have 2 carbon atoms because they involve double and triple bonds respectively which is not possible for a single carbon. Also, if we are using Pt or Pd as a catalyst then the reaction can be carried out at room temperatures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




