
What are maximum boiling azeotropes? Give one example.
Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint: An azeotrope is defined as a mixture of two liquids that has a constant boiling point and whose proportions cannot be changed by simple distillation. Maximum boiling azeotropes are those which have the boiling point higher than any of its constituents. For an azeotrope, the boiling point can be higher or lower than the constituents from which it is made.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
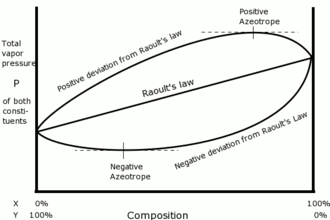
Azeotropes are of two types- minimum boiling azeotropes and maximum boiling azeotropes. A minimum boiling azeotrope shows greater positive deviation from Raoult’s Law and maximum boiling azeotrope shows negative deviation from Raoult’s Law. Negative deviation arises when vapor pressure of mixture is lower than as expected from Raoult’s law.
The example of Maximum boiling azeotrope is-the boiling point of hydrogen chloride is $-84{}^\circ C$ and that of water is $100{}^\circ C$ but their mixture i.e. the azeotrope formed boils at $110{}^\circ C$.
Additional Information:
Non ideal solutions are those which do not obey Raoult’s Law. They are of two kinds, the one showing positive deviation and the other showing negative deviation. Boiling point of an ideal solution lies in between the boiling point of its pure components. All non- ideal solutions do not form azeotropes, only the one deviating from Raoult’s Law forms. According to Raoult’s Law, the partial pressure for a component equals the product of its vapor pressure and mole fraction. When the two components are mixed their enthalpy should be zero which indicates that no heat is released or absorbed during mixing of two pure components to form an ideal solution.
Note: The composition of azeotropes in liquid and vapor phase remains the same due to which they cannot be separated by fractional distillation method. This is the reason why ideal solutions do not form azeotropes. Azeotrope is derived from a Greek word- ‘a’ meaning not, ‘zeo’ meaning boil and ‘tropic’ refers to change, so basically the one which can’t be changed by boiling or distillation.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
Azeotropes are of two types- minimum boiling azeotropes and maximum boiling azeotropes. A minimum boiling azeotrope shows greater positive deviation from Raoult’s Law and maximum boiling azeotrope shows negative deviation from Raoult’s Law. Negative deviation arises when vapor pressure of mixture is lower than as expected from Raoult’s law.
The example of Maximum boiling azeotrope is-the boiling point of hydrogen chloride is $-84{}^\circ C$ and that of water is $100{}^\circ C$ but their mixture i.e. the azeotrope formed boils at $110{}^\circ C$.

Additional Information:
Non ideal solutions are those which do not obey Raoult’s Law. They are of two kinds, the one showing positive deviation and the other showing negative deviation. Boiling point of an ideal solution lies in between the boiling point of its pure components. All non- ideal solutions do not form azeotropes, only the one deviating from Raoult’s Law forms. According to Raoult’s Law, the partial pressure for a component equals the product of its vapor pressure and mole fraction. When the two components are mixed their enthalpy should be zero which indicates that no heat is released or absorbed during mixing of two pure components to form an ideal solution.
Note: The composition of azeotropes in liquid and vapor phase remains the same due to which they cannot be separated by fractional distillation method. This is the reason why ideal solutions do not form azeotropes. Azeotrope is derived from a Greek word- ‘a’ meaning not, ‘zeo’ meaning boil and ‘tropic’ refers to change, so basically the one which can’t be changed by boiling or distillation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




