
Why are NOR gates considered as universal gates?
Answer
579.3k+ views
Hint: Draw the truth table for NOR gates. Try realising other basic gates with NOR gate. Combination of One or more NOR gates can give every other basic gates.
Complete step by step solution:
NOR gate is a logic gate that gives positive output (high) only when both the inputs are negative (low). It gives negative output (low) when any one of the input is positive (high). It also gives a negative output (low) when both the inputs are positive (high). It is called a universal gate as NOR gates can be combined to get every other basic logic gates.
Logic Expression for NOR gate is: $Y = \overline {A + B} $
The truth table for NOR gate is as follows:
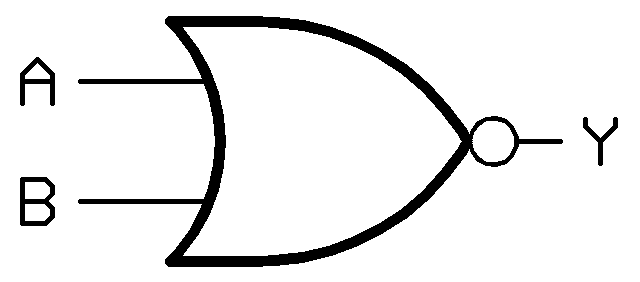
The logic symbol for NOR gate is:
Realising other gates using NOR gate:
i) AND gate:
AND gate is a gate that gives positive output (high) only when both the outputs are positive (high). In all other cases it gives a negative (low) output. When we create a circuit as shown in the figure, we realise that when both A and B are positive (high), the output from respective NOR gates are both negative (low). As a result the inputs for the final NOR gate are both negative and result in a positive output. This is in accordance with AND gate definition.
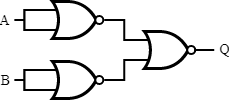
Thus by using 3 NOR gates we can develop an AND gate.
ii) OR gate:
OR gate is an operation that gives positive value when either one or both the inputs are positive. It gives a negative value only when both the inputs are negative.
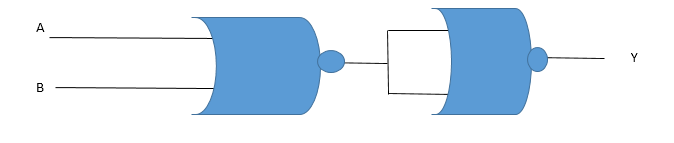
Thus, OR gate can be realised using 2 NOR gates.
iii) NOT gate:
NOT gate is an operation that inverts the input and then presents it as the output. Thus, for a positive input, the output is negative and vice versa.
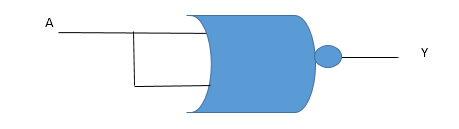
Thus NOT gate can be realised using NOR gate.
Since all the basic gates are realised using NOR gate, it is referred to as universal gate.
Note: All basic gates must be realised using nor gate alone and no other logic gates. NOR gate is nothing but OR + NOT. NOR gates can be applied in the mixer tank, it does the work of two gates alone and hence is economic. NAND is another universal gate.
Complete step by step solution:
NOR gate is a logic gate that gives positive output (high) only when both the inputs are negative (low). It gives negative output (low) when any one of the input is positive (high). It also gives a negative output (low) when both the inputs are positive (high). It is called a universal gate as NOR gates can be combined to get every other basic logic gates.
Logic Expression for NOR gate is: $Y = \overline {A + B} $
The truth table for NOR gate is as follows:
| Input 1 ( $A$ ) | Input 2 ( $B$ ) | OUTPUT $Y = \overline {A + B} $ |
| $0$ | $0$ | $1$ |
| $0$ | $1$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $1$ | $0$ |
The logic symbol for NOR gate is:

Realising other gates using NOR gate:
i) AND gate:
AND gate is a gate that gives positive output (high) only when both the outputs are positive (high). In all other cases it gives a negative (low) output. When we create a circuit as shown in the figure, we realise that when both A and B are positive (high), the output from respective NOR gates are both negative (low). As a result the inputs for the final NOR gate are both negative and result in a positive output. This is in accordance with AND gate definition.

| INPUT 1 ( $A$ ) | INPUT 2 ( $B$ ) | OUTPUT ( $Q = \overline {\overline {(A + A)} + \overline {(B + B} } )$ |
| $0$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $0$ | $1$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $1$ | $1$ | $1$ |
Thus by using 3 NOR gates we can develop an AND gate.
ii) OR gate:
OR gate is an operation that gives positive value when either one or both the inputs are positive. It gives a negative value only when both the inputs are negative.

| INPUT 1 ( $A$ ) | INPUT 2 ( $B$ ) | OUTPUT ( $Q = \overline {(\overline {A + B)} + (\overline {A + B} )} $ |
| $0$ | $0$ | $0$ |
| $0$ | $1$ | $1$ |
| $1$ | $0$ | $1$ |
| $1$ | $1$ | $1$ |
Thus, OR gate can be realised using 2 NOR gates.
iii) NOT gate:
NOT gate is an operation that inverts the input and then presents it as the output. Thus, for a positive input, the output is negative and vice versa.

| INPUT 1 ( $A$ ) | OUTPUT ( $Q = \overline {A + A} $ ) |
| $0$ | 1 |
| $1$ | $0$ |
Thus NOT gate can be realised using NOR gate.
Since all the basic gates are realised using NOR gate, it is referred to as universal gate.
Note: All basic gates must be realised using nor gate alone and no other logic gates. NOR gate is nothing but OR + NOT. NOR gates can be applied in the mixer tank, it does the work of two gates alone and hence is economic. NAND is another universal gate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




