
Why are Ortho, Meta and Para not used in IUPAC nomenclature?
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: IUPAC is a worldwide accepted naming system. We use Ortho, Meta and Para terms for common naming of benzene derived compounds. IUPAC names the benzene derived compounds based on the simple benzene naming system.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that IUPAC nomenclature is a method of naming chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
We use the terms ortho, meta and para while naming benzene derived compounds. Ortho, meta and para are basically -1,2 -1,3 and 1,4 position of the substituents with respect to the other functional group on the benzene ring. Let us take an example of aniline with a nitro- substituent to understand the ortho, meta and para positioning-
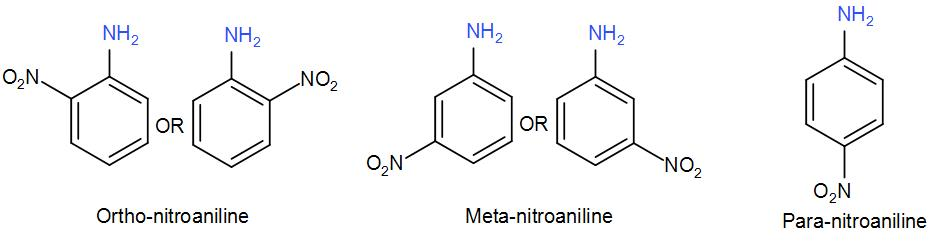
Instead of using numbers, we use the terms Ortho, Meta and Para to name such di-substituted benzene compounds.
However, we use these terms only for the common names of the respective compound.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, abbreviated as IUPAC relies on the nomenclature of various benzene derived compounds on the simple benzene naming system therefore, Ortho, Meta and Para terms are not accepted by the IUPAC. Compounds with Ortho, Meta or Para substitutions are named according to the common benzene system and can be converted to systematic names.
For example, aniline is the common preferred IUPAC name and its systematic IUPAC name is benzamine. Ortho-nitroaniline is the common name for 2-Nitronianiline, Meta-nitroaniline is 3-Nitroaniline and Para-nitroaniline is 4-Nitroaniline.
Note: If two substituents occupy position next to each other then they are called ortho substituents to each other. If there is a gap of one carbon atom between the two substituents then they are meta and if they are across each other in a benzene ring i.e. there is a gap of two carbon atoms between them then they are para to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that IUPAC nomenclature is a method of naming chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry.
We use the terms ortho, meta and para while naming benzene derived compounds. Ortho, meta and para are basically -1,2 -1,3 and 1,4 position of the substituents with respect to the other functional group on the benzene ring. Let us take an example of aniline with a nitro- substituent to understand the ortho, meta and para positioning-

Instead of using numbers, we use the terms Ortho, Meta and Para to name such di-substituted benzene compounds.
However, we use these terms only for the common names of the respective compound.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, abbreviated as IUPAC relies on the nomenclature of various benzene derived compounds on the simple benzene naming system therefore, Ortho, Meta and Para terms are not accepted by the IUPAC. Compounds with Ortho, Meta or Para substitutions are named according to the common benzene system and can be converted to systematic names.
For example, aniline is the common preferred IUPAC name and its systematic IUPAC name is benzamine. Ortho-nitroaniline is the common name for 2-Nitronianiline, Meta-nitroaniline is 3-Nitroaniline and Para-nitroaniline is 4-Nitroaniline.
Note: If two substituents occupy position next to each other then they are called ortho substituents to each other. If there is a gap of one carbon atom between the two substituents then they are meta and if they are across each other in a benzene ring i.e. there is a gap of two carbon atoms between them then they are para to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




