
What are Plasmodesmata and Desmosomes?
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: Cell membrane is the outer membranous covering of the protoplast or cell protoplasm. Cell membrane is also called a plasma membrane. To serve special types of functions the cell membrane has to be modified. The common modifications are – microvilli, lomasomes, sheaths, pores, intercellular junctions.
Complete Answer-
Intercellular junctions are contacts between adjacent cells which in case of animal cells are separated by narrow intercellular spaces and contain tissue fluid. The important ones are – Interdigitations, Intercellular Bridges, Tight Junctions, Gap Junctions, Desmosomes, Terminal Bars, Plasmodesmata.
Now, we talk about only the two in detail –
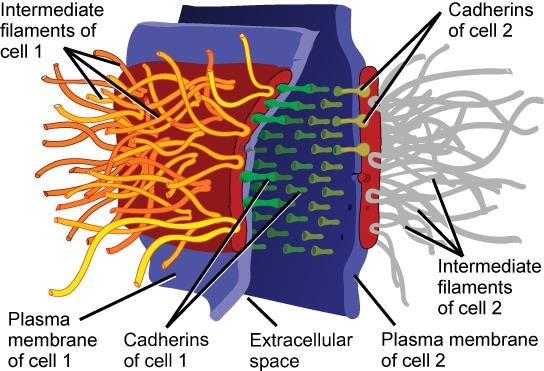
1. Desmosomes: These are circular regions where adjacent membranes possess disc-shaped thickening on the inner side, a number of tonofibrils and trans-membrane linkers embedded in dense intercellular material. They act as ‘spot welds’ and keep the cells firmly together. They occur in epithelia subjected to disruption. They are found in cardiac muscle, epithelia, etc. and they are also known as Macula Adherens.
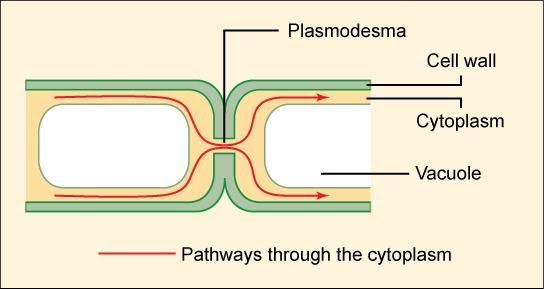
2. Plasmodesmata: These are protoplasmic bridges amongst plant cells which occur in the areas of cell wall pits or pores. Materials may pass from cell to cell through plasmodesmata. They form a protoplasmic continuum called symplast. A plasmodesmata consists of a canal, having a simple or branched tubule called a desmotubule. Desmotubule is an extension of the endoplasmic reticulum. Plasmodesmata is basically of two types:
Primary – These are formed at the time of cell division and responsible for growth and development.
Secondary – They are formed between mature cells and they share different functional properties.
Note:
Functions of cell membrane:
- It protects cells from injury.
- It forms various types of junctions to keep the cells together.
- By forming plasmodesmata, the cell membranes establish cytoplasmic continuity between adjacent cells.
Complete Answer-
Intercellular junctions are contacts between adjacent cells which in case of animal cells are separated by narrow intercellular spaces and contain tissue fluid. The important ones are – Interdigitations, Intercellular Bridges, Tight Junctions, Gap Junctions, Desmosomes, Terminal Bars, Plasmodesmata.
Now, we talk about only the two in detail –
1. Desmosomes: These are circular regions where adjacent membranes possess disc-shaped thickening on the inner side, a number of tonofibrils and trans-membrane linkers embedded in dense intercellular material. They act as ‘spot welds’ and keep the cells firmly together. They occur in epithelia subjected to disruption. They are found in cardiac muscle, epithelia, etc. and they are also known as Macula Adherens.

2. Plasmodesmata: These are protoplasmic bridges amongst plant cells which occur in the areas of cell wall pits or pores. Materials may pass from cell to cell through plasmodesmata. They form a protoplasmic continuum called symplast. A plasmodesmata consists of a canal, having a simple or branched tubule called a desmotubule. Desmotubule is an extension of the endoplasmic reticulum. Plasmodesmata is basically of two types:
Primary – These are formed at the time of cell division and responsible for growth and development.
Secondary – They are formed between mature cells and they share different functional properties.

Note:
Functions of cell membrane:
- It protects cells from injury.
- It forms various types of junctions to keep the cells together.
- By forming plasmodesmata, the cell membranes establish cytoplasmic continuity between adjacent cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




