
Why are root nodules useful for plants?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Root nodules are found primarily in leguminous plants. Root nodules help plants to survive in nitrogen-limiting conditions. The association of bacteria and legume plants is a symbiotic relationship.
Complete answer:
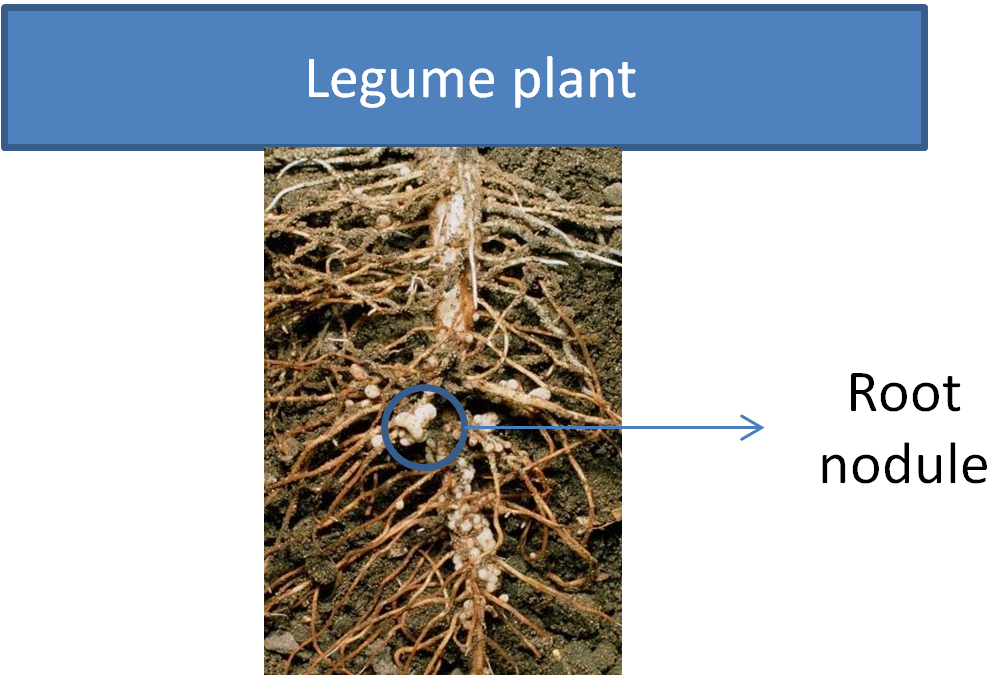
This symbiotic relation between root nodules and bacteria of the leguminous plants makes legumes an ideal agricultural organism as their requirement for nitrogen fertilizer is reduced. Within root nodules, nitrogen gas ($N_2$) from the atmosphere is reduced to ammonia ($NH_3$), which is then assimilated into amino acids, nucleotides, and other cellular components such as vitamins, flavonoids, and hormones.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins while nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The energy for reducing the nitrogen gas in the nodule comes from the sugar which is a product of photosynthesis synthesized in leaves and is further translocated from the leaf.
Root nodules have a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of Rhizobia and play a key role in crop rotation.
Additional Information:
-A legume is a plant belonging to the Fabaceae family. When used as a dry grain, the seed is known as a pulse. They have grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption and for livestock forage.
-Legumes are also soil-enhancing green manure.
-Legume crops include beans, peas, soybeans, chickpea, pigeon pea, alfalfa, clover, peanuts, lentils, tamarind, etc.
-This association has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade.
Note:
-Nitrogen fixation in the root nodule by the bacteria is a very oxygen-sensitive process.
-Legume nodules have a special iron-containing protein called leghemoglobin which is closely related to animal myoglobin.
-There are two main types of nodules found- determinate nodules, which lose meristematic activity shortly after initiation and growth is due to expansion of cell and indeterminate nodules, which maintain an active apical meristem that produces new cells in plants.
Complete answer:
This symbiotic relation between root nodules and bacteria of the leguminous plants makes legumes an ideal agricultural organism as their requirement for nitrogen fertilizer is reduced. Within root nodules, nitrogen gas ($N_2$) from the atmosphere is reduced to ammonia ($NH_3$), which is then assimilated into amino acids, nucleotides, and other cellular components such as vitamins, flavonoids, and hormones.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins while nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. The energy for reducing the nitrogen gas in the nodule comes from the sugar which is a product of photosynthesis synthesized in leaves and is further translocated from the leaf.
Root nodules have a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of Rhizobia and play a key role in crop rotation.

Additional Information:
-A legume is a plant belonging to the Fabaceae family. When used as a dry grain, the seed is known as a pulse. They have grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption and for livestock forage.
-Legumes are also soil-enhancing green manure.
-Legume crops include beans, peas, soybeans, chickpea, pigeon pea, alfalfa, clover, peanuts, lentils, tamarind, etc.
-This association has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade.
Note:
-Nitrogen fixation in the root nodule by the bacteria is a very oxygen-sensitive process.
-Legume nodules have a special iron-containing protein called leghemoglobin which is closely related to animal myoglobin.
-There are two main types of nodules found- determinate nodules, which lose meristematic activity shortly after initiation and growth is due to expansion of cell and indeterminate nodules, which maintain an active apical meristem that produces new cells in plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




