
What are some examples of structural polysaccharides?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: Biomacromolecules are large biological polymers made up of monomers linked together, such as nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates. Proteins, for example, are made up of monomers called amino acids.
Complete answer:
Polysaccharides are large macromolecules made up of monosaccharide chains. These chains are held together by glycosidic bonds. Simple sugars glucose, fructose, mannose, and galactose are common monomer units in polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides can be divided into two categories:
1. Homo-polysaccharides: Homo-polysaccharides are polysaccharide units made up of the same type of monosaccharide. cellulose, starch, and glycogen, for example.
2. Hetero-polysaccharides: Hetero-polysaccharides are polysaccharides made up of two or more monosaccharide units. They provide extracellular support for organisms, such as hyaluronic acid.
All polysaccharides are created by the same basic process, which involves the formation of glycosidic bonds between monosaccharides. An oxygen molecule connects two carbon rings in these glycosidic bonds. The bond is formed when a hydroxyl group is removed from one molecule's carbon, and the hydrogen is removed from another monosaccharide's hydroxyl group.
When we say cellulose, pectin, or chitin, you're probably thinking of cellulose, pectin, or chitin. All of these polysaccharides are structural polysaccharides. Arabinoxylans are another example. Cellulose, pectin, and arabinoxylans are mostly found in plants, whereas chitin is found in animal exoskeletons. When we eat table sugar, we consume cellulose (sucrose). Sugars from cane or beets are used to make it.
Thus, Cellulose and chitin are examples of structural polysaccharides.
Following image shows the structure of Cellulose:

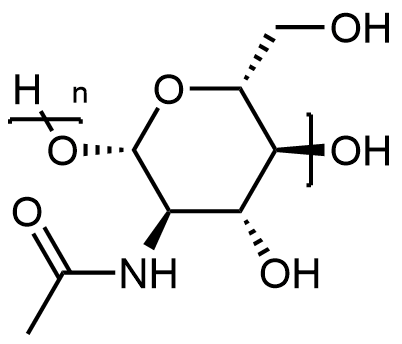
Following is the structure of chitin:
Note:
Polysaccharides play an important role in cell structure and function.
1. Storage polysaccharides: Storage polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, are polysaccharides that are stored in the liver and muscles to be converted to energy for body functions later. Plants contain starch, whereas animals contain glycogen.
2. Structural polysaccharides: Polysaccharides like cellulose, which are structural polysaccharides found in plant cell walls, are structural polysaccharides. Chitin is another structural polysaccharide.
Complete answer:
Polysaccharides are large macromolecules made up of monosaccharide chains. These chains are held together by glycosidic bonds. Simple sugars glucose, fructose, mannose, and galactose are common monomer units in polysaccharides.
Polysaccharides can be divided into two categories:
1. Homo-polysaccharides: Homo-polysaccharides are polysaccharide units made up of the same type of monosaccharide. cellulose, starch, and glycogen, for example.
2. Hetero-polysaccharides: Hetero-polysaccharides are polysaccharides made up of two or more monosaccharide units. They provide extracellular support for organisms, such as hyaluronic acid.
All polysaccharides are created by the same basic process, which involves the formation of glycosidic bonds between monosaccharides. An oxygen molecule connects two carbon rings in these glycosidic bonds. The bond is formed when a hydroxyl group is removed from one molecule's carbon, and the hydrogen is removed from another monosaccharide's hydroxyl group.
When we say cellulose, pectin, or chitin, you're probably thinking of cellulose, pectin, or chitin. All of these polysaccharides are structural polysaccharides. Arabinoxylans are another example. Cellulose, pectin, and arabinoxylans are mostly found in plants, whereas chitin is found in animal exoskeletons. When we eat table sugar, we consume cellulose (sucrose). Sugars from cane or beets are used to make it.
Thus, Cellulose and chitin are examples of structural polysaccharides.
Following image shows the structure of Cellulose:

Following is the structure of chitin:

Note:
Polysaccharides play an important role in cell structure and function.
1. Storage polysaccharides: Storage polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen, are polysaccharides that are stored in the liver and muscles to be converted to energy for body functions later. Plants contain starch, whereas animals contain glycogen.
2. Structural polysaccharides: Polysaccharides like cellulose, which are structural polysaccharides found in plant cell walls, are structural polysaccharides. Chitin is another structural polysaccharide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




