
What are some functions of plastids?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: Plastid is a double membraned organelle that is used to perform photosynthesis, attract pollinators, restore total leaf protein and synthesize starch along with the storage of proteins, fats, and oils.
Complete Answer:
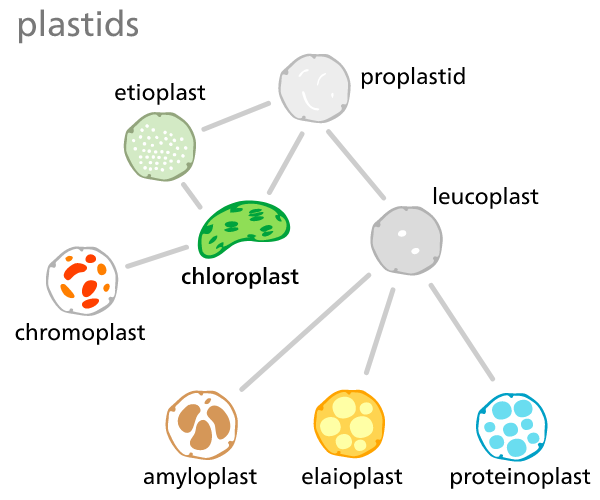
Plastids are DNA containing double membraned structures. One type of plastid shows similarity with mitochondria. Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plant cells containing DNA, their plasma membrane is double layer like mitochondria. Plastids store a variety of substances and are classified into three types, this classification was given by Haeckel:
A) Leucoplasts: These are the largest of all plastids, they are colorless. Depending upon the components stored in leucoplasts, it's of three types:
B) Amyloplast: Carbohydrate is stored within the sort of starch.
C) Aleuroplasts: Proteins are stored here. It is also referred to as the proteinoplast.
D) Oils and fat storage occur in them.
E) Chromoplast: Coloured pigments are stored in chromoplasts. They contain carotenoids which are fat-soluble. They give color to flowers and therefore help in the attraction of pollinators and dispersers of seeds and fruits.
F) Chloroplast: It is a semi-autonomous organelle in the plant cell. It is the most photosynthetic organ in plants and thus is additionally referred to as the kitchen of the cell.
Chloroplasts may be further divided on the basis of the color of the pigment;
(a) Chloroplasts:- It contains chlorophyll and is found mainly in the cells of the leaves of higher plants.
(b) Phaeoplasts:- These are yellow or brown plastids found in brown algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates.
(c) Rhodoplasts:- These are red colored plastids. It is found in red algae. It also absorbs light.
Additional Information regarding plastids :
The chloroplast is also a semi-autonomous cell organelle like mitochondria.
The chloroplast is semi-autonomous because it has the following two features:
a. It has its DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
b. It also has its protein-synthesizing machinery.
Chloroplast has different shapes in different organisms. Cup-shaped, girdle shapes, spiral, stellate, reticulate, and discoidal shapes of chloroplast have been observed.
Note:
Of the three types of plastids, leucoplast, chromoplast, and chloroplast, the only chloroplast is semi-autonomous and not the others. It is believed that these semi-autonomous organelles have originated from unicellular prokaryotes during evolution.
Complete Answer:
Plastids are DNA containing double membraned structures. One type of plastid shows similarity with mitochondria. Plastids are the largest cell organelle in plant cells containing DNA, their plasma membrane is double layer like mitochondria. Plastids store a variety of substances and are classified into three types, this classification was given by Haeckel:
A) Leucoplasts: These are the largest of all plastids, they are colorless. Depending upon the components stored in leucoplasts, it's of three types:
B) Amyloplast: Carbohydrate is stored within the sort of starch.
C) Aleuroplasts: Proteins are stored here. It is also referred to as the proteinoplast.
D) Oils and fat storage occur in them.
E) Chromoplast: Coloured pigments are stored in chromoplasts. They contain carotenoids which are fat-soluble. They give color to flowers and therefore help in the attraction of pollinators and dispersers of seeds and fruits.
F) Chloroplast: It is a semi-autonomous organelle in the plant cell. It is the most photosynthetic organ in plants and thus is additionally referred to as the kitchen of the cell.

Chloroplasts may be further divided on the basis of the color of the pigment;
(a) Chloroplasts:- It contains chlorophyll and is found mainly in the cells of the leaves of higher plants.
(b) Phaeoplasts:- These are yellow or brown plastids found in brown algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates.
(c) Rhodoplasts:- These are red colored plastids. It is found in red algae. It also absorbs light.
Additional Information regarding plastids :
The chloroplast is also a semi-autonomous cell organelle like mitochondria.
The chloroplast is semi-autonomous because it has the following two features:
a. It has its DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
b. It also has its protein-synthesizing machinery.
Chloroplast has different shapes in different organisms. Cup-shaped, girdle shapes, spiral, stellate, reticulate, and discoidal shapes of chloroplast have been observed.
Note:
Of the three types of plastids, leucoplast, chromoplast, and chloroplast, the only chloroplast is semi-autonomous and not the others. It is believed that these semi-autonomous organelles have originated from unicellular prokaryotes during evolution.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




