
What are stomata? Write its functions?
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: They are the specialized cells that perfect specific function and help in gaseous exchange in plant tissues.
Complete answer:
Stomata are the tiny openings or pores in plant tissues that allow gaseous exchange. They are typically found in plant leaves or sometimes may also be found in some stems.
There are various types of stomata:
- Anomocytic Stomata: They are surrounded by epidermal cells with fixed shape and size.
- Anisocytic Stomata: Each stoma is surrounded by unequal sized three subsidiary cells.
- Diacytic Stomata: These are surrounded by a pair of subsidiary cells that are perpendicular to guard cells.
- Paracytic Stomata: They are surrounded by two subsidiary cells.
- Gramineous Stomata: Each stoma possesses two guard cells.
Structure of Stomata
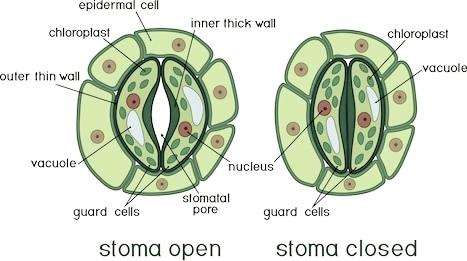
- Stomata have small openings surrounded by a pair of guard cells.
- Guard cells are specialized, bean-shaped cells surrounded by the stoma.
- The subsidiary cells are called accessory cells. They are found in plant epidermis.
- The opening and closing of stomata depend upon the turgor pressure.
- When the guard cells are expanded the stoma opens and closes when the guard cells lose water.
- Stomata normally open during light and close during the night.
Functions of Stomata
- Its main function is the exchange of gases by opening and closing the pores in the leaves.
- It helps in removing water from the leaves.
- It takes carbon dioxide and gives out oxygen during the process of photosynthesis.
- It helps in regulating water movement through transpiration.
Stomata facilitates gaseous exchange. It is responsible for the processes of making food in plants.
Note: To avoid photorespiration there should be a wide stomatal aperture to increase carbon dioxide content or else more energy and carbon dioxide will be wasted.
Complete answer:
Stomata are the tiny openings or pores in plant tissues that allow gaseous exchange. They are typically found in plant leaves or sometimes may also be found in some stems.
There are various types of stomata:
- Anomocytic Stomata: They are surrounded by epidermal cells with fixed shape and size.
- Anisocytic Stomata: Each stoma is surrounded by unequal sized three subsidiary cells.
- Diacytic Stomata: These are surrounded by a pair of subsidiary cells that are perpendicular to guard cells.
- Paracytic Stomata: They are surrounded by two subsidiary cells.
- Gramineous Stomata: Each stoma possesses two guard cells.
Structure of Stomata
- Stomata have small openings surrounded by a pair of guard cells.
- Guard cells are specialized, bean-shaped cells surrounded by the stoma.
- The subsidiary cells are called accessory cells. They are found in plant epidermis.
- The opening and closing of stomata depend upon the turgor pressure.
- When the guard cells are expanded the stoma opens and closes when the guard cells lose water.
- Stomata normally open during light and close during the night.
Functions of Stomata
- Its main function is the exchange of gases by opening and closing the pores in the leaves.
- It helps in removing water from the leaves.
- It takes carbon dioxide and gives out oxygen during the process of photosynthesis.
- It helps in regulating water movement through transpiration.

Stomata facilitates gaseous exchange. It is responsible for the processes of making food in plants.
Note: To avoid photorespiration there should be a wide stomatal aperture to increase carbon dioxide content or else more energy and carbon dioxide will be wasted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




