
What are the changes seen in the Ovule and Ovary after Fertilization?
Answer
500.4k+ views
Hint: After fertilization, various changes occur in ovaries and ovules. The ovary develops into the edible part of the plant which is the characteristic feature of angiosperm whereas ovules develop into an embryonic plant which is enclosed in a protective covering.
Complete answer:
Fertilisation is defined as the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism.
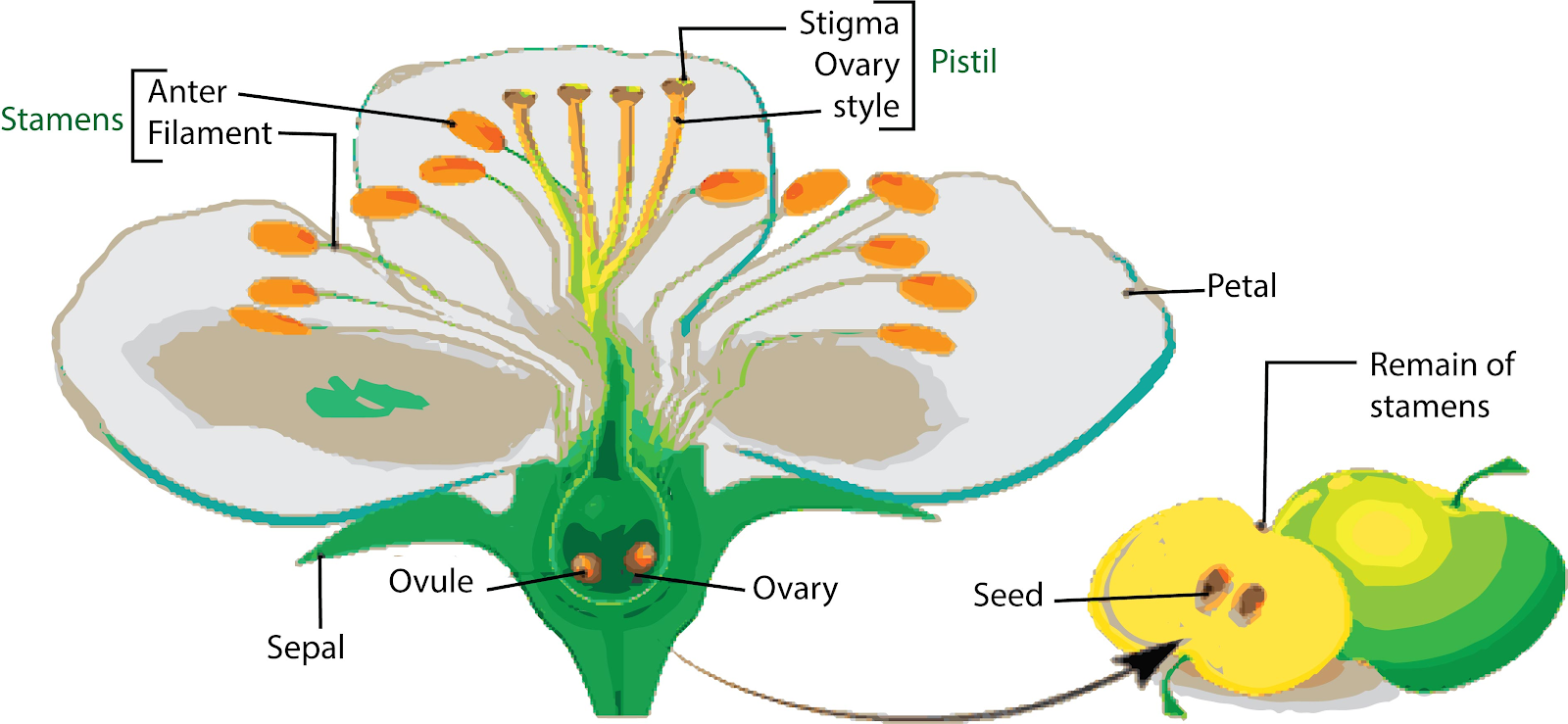
As fertilization occurs, the zygote is formed which later develops into an embryo. The ovary develops into a fruit and the ovule develops into a seed after fertilization. As the embryo develops, the fertilized ovule develops into a seed. A typical seed consists of a seed coat, endosperm, and embryo.
The seed coat develops from the integuments of ovules. Its major function is to give protection to the embryo.
The endosperm is a product of triple fusion and develops from the central cell of the embryo sack. It is generally a triploid tissue and provides reserve food material and nutrition to the developing embryo.
Embryo gives rise to mature plants and maintains the continuity of the generation.
A Fruit is a ripened ovary. The wall of the ovary forms the fruit wall, also called the pericarp.
Fruit may be true fruit or a false fruit or a parthenocarpic fruit.
- True Fruit develops from the ovary. For example, mango.
- False Fruit develops from the floral part and thalamus along with the development of the ovary wall. For example, apples.
- Parthenocarpic fruits are the fruits that develop without fertilization. They are seedless and can also be produced with the help of growth hormones like Auxins. For example, bananas.
Note:
- A seed can be endospermic where the endosperm persists after the seed formation and it can also be non-endospermic where the embryo uses up all the endosperm before the development of the seed.
- A seed coat has two layers, outer Testa and inner tegmen. There is a micropyle which remains as a small coat in the seed. During germination, micropyle facilitates the entry of oxygen and water into the seed.
- The first stimulus for fruit development comes from pollination while the second stimulus is received from developing seed and the third stimulus is provided by the availability of nutrients.
Complete answer:
Fertilisation is defined as the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism.
As fertilization occurs, the zygote is formed which later develops into an embryo. The ovary develops into a fruit and the ovule develops into a seed after fertilization. As the embryo develops, the fertilized ovule develops into a seed. A typical seed consists of a seed coat, endosperm, and embryo.
The seed coat develops from the integuments of ovules. Its major function is to give protection to the embryo.
The endosperm is a product of triple fusion and develops from the central cell of the embryo sack. It is generally a triploid tissue and provides reserve food material and nutrition to the developing embryo.
Embryo gives rise to mature plants and maintains the continuity of the generation.
A Fruit is a ripened ovary. The wall of the ovary forms the fruit wall, also called the pericarp.
Fruit may be true fruit or a false fruit or a parthenocarpic fruit.
- True Fruit develops from the ovary. For example, mango.
- False Fruit develops from the floral part and thalamus along with the development of the ovary wall. For example, apples.
- Parthenocarpic fruits are the fruits that develop without fertilization. They are seedless and can also be produced with the help of growth hormones like Auxins. For example, bananas.
Note:
- A seed can be endospermic where the endosperm persists after the seed formation and it can also be non-endospermic where the embryo uses up all the endosperm before the development of the seed.
- A seed coat has two layers, outer Testa and inner tegmen. There is a micropyle which remains as a small coat in the seed. During germination, micropyle facilitates the entry of oxygen and water into the seed.
- The first stimulus for fruit development comes from pollination while the second stimulus is received from developing seed and the third stimulus is provided by the availability of nutrients.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




