
What are the cis and trans isomers of $2 - {\text{butene}}$?
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: $2 - {\text{butene}}$ is an alkene which exists as two versions: ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}$ and ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}{\text{.}}$ These two forms are conformational isomers, their structure differing in the position of the two terminal methyl groups. In ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the aforementioned methyl groups are on the same side, whereas in ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the methyl groups are on opposite sides.
Complete answer:
$2 - {\text{butene}}$ is an alkene containing $4$ carbon atoms. It has the molecular formula \[{C_4}{H_8}\]. This alkene is acyclic in nature, and is the simplest alkene to exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
Cis-trans isomerism, also known as E-Z isomerism, is a term used in organic chemistry and a property shown by both organic and inorganic molecules. It is a type of isomerism falling under the category of stereoisomerism, where atoms have different spatial arrangement in three dimensional space. The prefixes “cis” and “trans” have latin roots, cis being translated to “this side of”, and trans being translated to “other side of”. In organic chemistry, cis isomers have functional groups on the same side of the carbon chain, while trans isomers have functional groups on the opposite sides of the carbon chain.
The diagram shown below has the pictorial representation of ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}$ and ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}{\text{.}}$
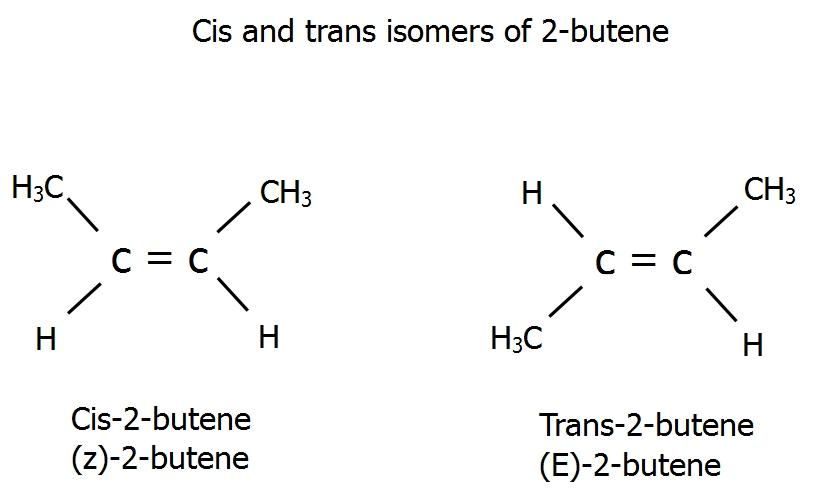
It is clear that in ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the terminal methyl groups (at positions 1 and 4), are on the same side of the carbon chain, while in ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the terminal methyl groups are on the opposite sides of the carbon chain. Hence, we have successfully explained and diagrammatically represented the cis and trans isomers of $2 - {\text{butene}}{\text{.}}$
Note:
In principle, the cis and trans isomers of butene are conformational isomers, but theoretically, they can be interconverted by a simple rotation about the double bond. However, this rotation is not feasible, as the energy requirement of \[66{\text{ }}kcal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\] is quite high. This requirement is not met under normal conditions of its existence.
Complete answer:
$2 - {\text{butene}}$ is an alkene containing $4$ carbon atoms. It has the molecular formula \[{C_4}{H_8}\]. This alkene is acyclic in nature, and is the simplest alkene to exhibit cis-trans isomerism.
Cis-trans isomerism, also known as E-Z isomerism, is a term used in organic chemistry and a property shown by both organic and inorganic molecules. It is a type of isomerism falling under the category of stereoisomerism, where atoms have different spatial arrangement in three dimensional space. The prefixes “cis” and “trans” have latin roots, cis being translated to “this side of”, and trans being translated to “other side of”. In organic chemistry, cis isomers have functional groups on the same side of the carbon chain, while trans isomers have functional groups on the opposite sides of the carbon chain.
The diagram shown below has the pictorial representation of ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}$ and ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene}}{\text{.}}$

It is clear that in ${\text{cis}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the terminal methyl groups (at positions 1 and 4), are on the same side of the carbon chain, while in ${\text{trans}} - 2 - {\text{butene,}}$ the terminal methyl groups are on the opposite sides of the carbon chain. Hence, we have successfully explained and diagrammatically represented the cis and trans isomers of $2 - {\text{butene}}{\text{.}}$
Note:
In principle, the cis and trans isomers of butene are conformational isomers, but theoretically, they can be interconverted by a simple rotation about the double bond. However, this rotation is not feasible, as the energy requirement of \[66{\text{ }}kcal\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\] is quite high. This requirement is not met under normal conditions of its existence.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




