
What are the definitions of condensation reaction?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: A condensation reaction in organic chemistry is the joining of two molecules to produce a single molecule, usually with the loss of a minor molecule like water. The reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis when water is lost. Other molecules, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid, and hydrogen sulphide, can also be lost.
Complete answer:
The two molecules are normally added to the addition product in a step-by-step method, usually in equilibrium and with the loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). A diverse family of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic circumstances or in the presence of a catalyst, the reaction may otherwise include the functional groups of the molecule. This group of events is necessary for the creation of peptide bonds between amino acids and the production of fatty acids, therefore thus is a necessary part of life.
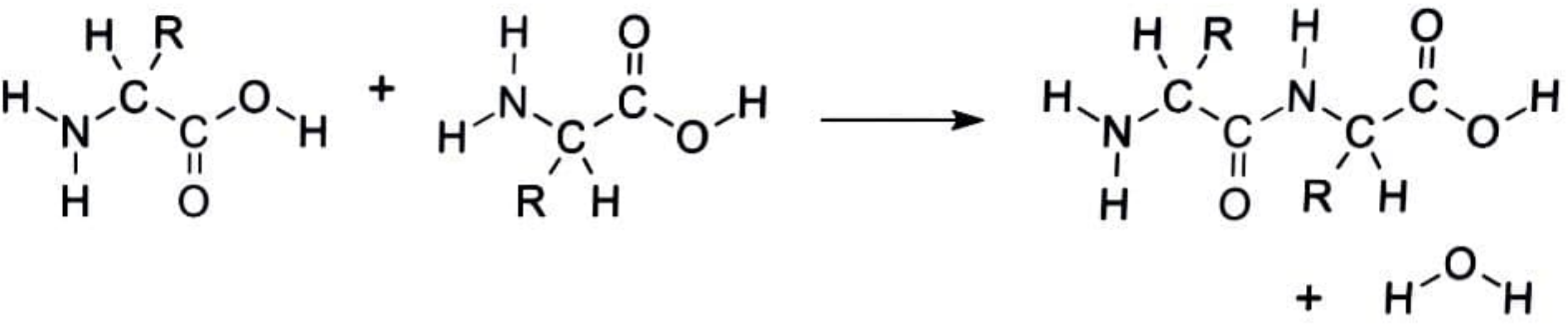
fig.condensation of two amino acids to give a peptide bond.
Condensation reactions can be in a variety of forms. Aldol condensation and Knoevenagel condensation, both of which produce water as a by-product, as well as the Claisen condensation and the Dieckman condensation (intramolecular Claisen condensation), all of which produce alcohols as by-products, are common examples.
Note:
A condensation reaction in organic chemistry is the joining of two molecules to produce a single molecule, usually with the loss of a minor molecule like water. The reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis when water is lost.
Complete answer:
The two molecules are normally added to the addition product in a step-by-step method, usually in equilibrium and with the loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). A diverse family of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic circumstances or in the presence of a catalyst, the reaction may otherwise include the functional groups of the molecule. This group of events is necessary for the creation of peptide bonds between amino acids and the production of fatty acids, therefore thus is a necessary part of life.

fig.condensation of two amino acids to give a peptide bond.
Condensation reactions can be in a variety of forms. Aldol condensation and Knoevenagel condensation, both of which produce water as a by-product, as well as the Claisen condensation and the Dieckman condensation (intramolecular Claisen condensation), all of which produce alcohols as by-products, are common examples.
Note:
A condensation reaction in organic chemistry is the joining of two molecules to produce a single molecule, usually with the loss of a minor molecule like water. The reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis when water is lost.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




