
How many are the examples of rhizomes
Ginger, turmeric, canna, waterlily, banana, colocasia, alocasia, colchicum, saffron.
(a) Two
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Eight
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: plants that contain underground modified stems that store food which is developed from the auxiliary and grows horizontally and gives rise to a new plant.
Complete answer:
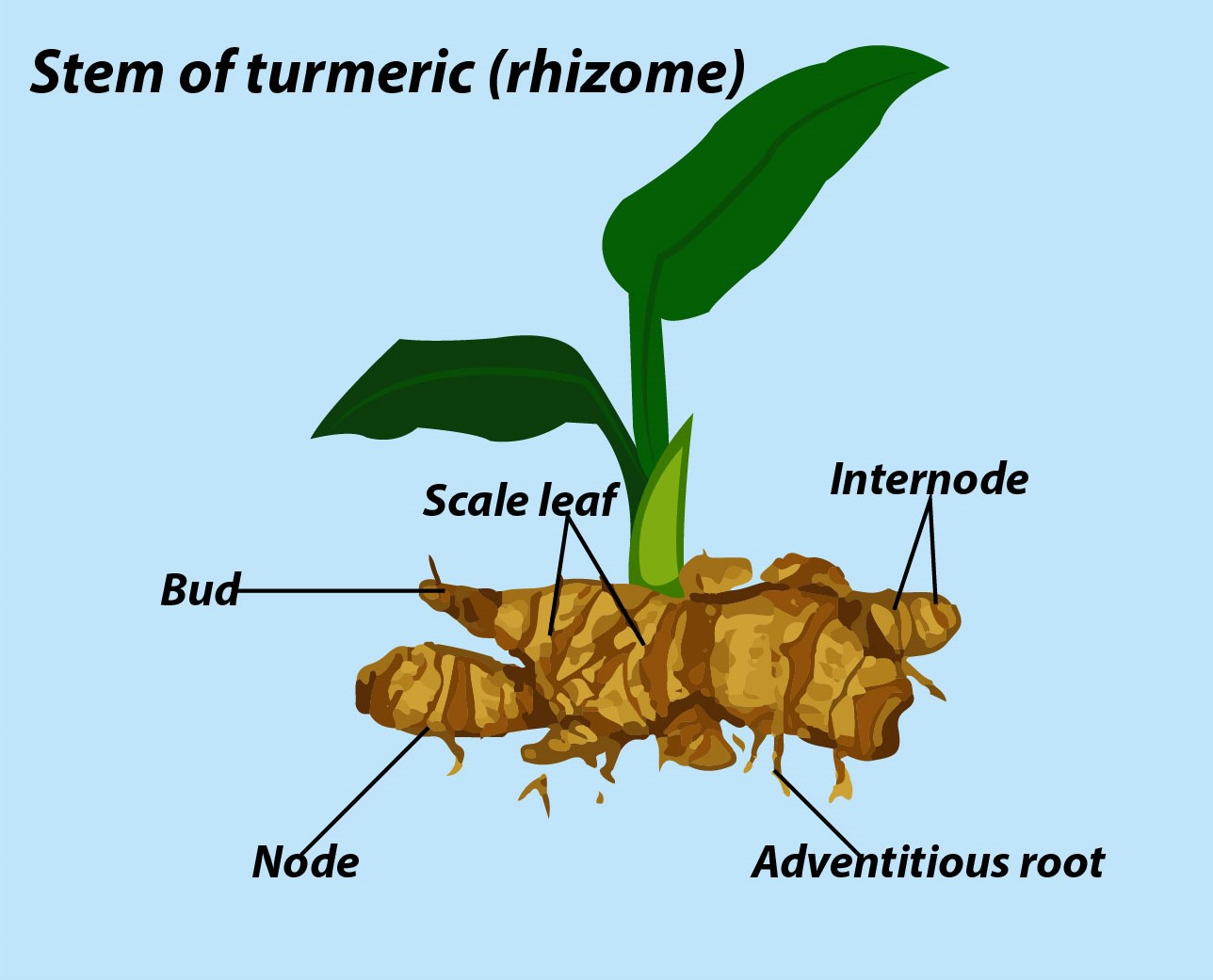
The main function of the stem is to spread out branches that bear leaves, flowers, and fruits. It also helps in the conduction of water and minerals and photosynthates. But in some plants, the stem is modified to perform other functions like storage of food, vegetative propagation, giving mechanical support, and protection. Some of the underground stem modifications are stem tuber, rhizome, corm, and bulb. The stems that develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally give rise to a new plant is called a rhizome. Ginger, turmeric, canna, and banana are examples of rhizomes.
Additional Information: - In order to survive in unfavorable conditions, vegetative parts like roots, stems, and leaves in plants undergo some modifications.
- Roots in plants are modified to prop roots, stilt roots, pneumatic roots, velamen roots, haustorial roots, nodular roots, photosynthetic roots.
- Underground stems are modified into stem tuber, rhizome, corm, and bulb, aerial stems are modified into stem tendrils, thorns, phylloclades, cladophylls, and bulbils.
- Ginger, turmeric, canna, and banana are examples of rhizomes; water lily is an example of thorns; colocasia, alocasia, and saffron are examples of corm
So, the correct answer is ‘four’
Note: -Not only roots and stem of the plant undergo modification but leaves also get modified to tendrils, spines, phyllodes, insectivorous leaves, and leaves that help in vegetative propagation.
-In colchicum, leaves are modified to tendrils.
-Other examples of stem modification are amorphophallus for corm, onions for bulbs, and

Complete answer:
The main function of the stem is to spread out branches that bear leaves, flowers, and fruits. It also helps in the conduction of water and minerals and photosynthates. But in some plants, the stem is modified to perform other functions like storage of food, vegetative propagation, giving mechanical support, and protection. Some of the underground stem modifications are stem tuber, rhizome, corm, and bulb. The stems that develop from axillary buds and grow horizontally give rise to a new plant is called a rhizome. Ginger, turmeric, canna, and banana are examples of rhizomes.
Additional Information: - In order to survive in unfavorable conditions, vegetative parts like roots, stems, and leaves in plants undergo some modifications.
- Roots in plants are modified to prop roots, stilt roots, pneumatic roots, velamen roots, haustorial roots, nodular roots, photosynthetic roots.
- Underground stems are modified into stem tuber, rhizome, corm, and bulb, aerial stems are modified into stem tendrils, thorns, phylloclades, cladophylls, and bulbils.
- Ginger, turmeric, canna, and banana are examples of rhizomes; water lily is an example of thorns; colocasia, alocasia, and saffron are examples of corm
So, the correct answer is ‘four’
Note: -Not only roots and stem of the plant undergo modification but leaves also get modified to tendrils, spines, phyllodes, insectivorous leaves, and leaves that help in vegetative propagation.
-In colchicum, leaves are modified to tendrils.
-Other examples of stem modification are amorphophallus for corm, onions for bulbs, and


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




