
What are the functions of Sertoli cells of the seminiferous tubules and the Leydig cells in a man?
Answer
525.7k+ views
Hint: These cells are supportive cells and aid in the formation of gametes and regulation of primary and secondary sexual characters.
Complete Answer:
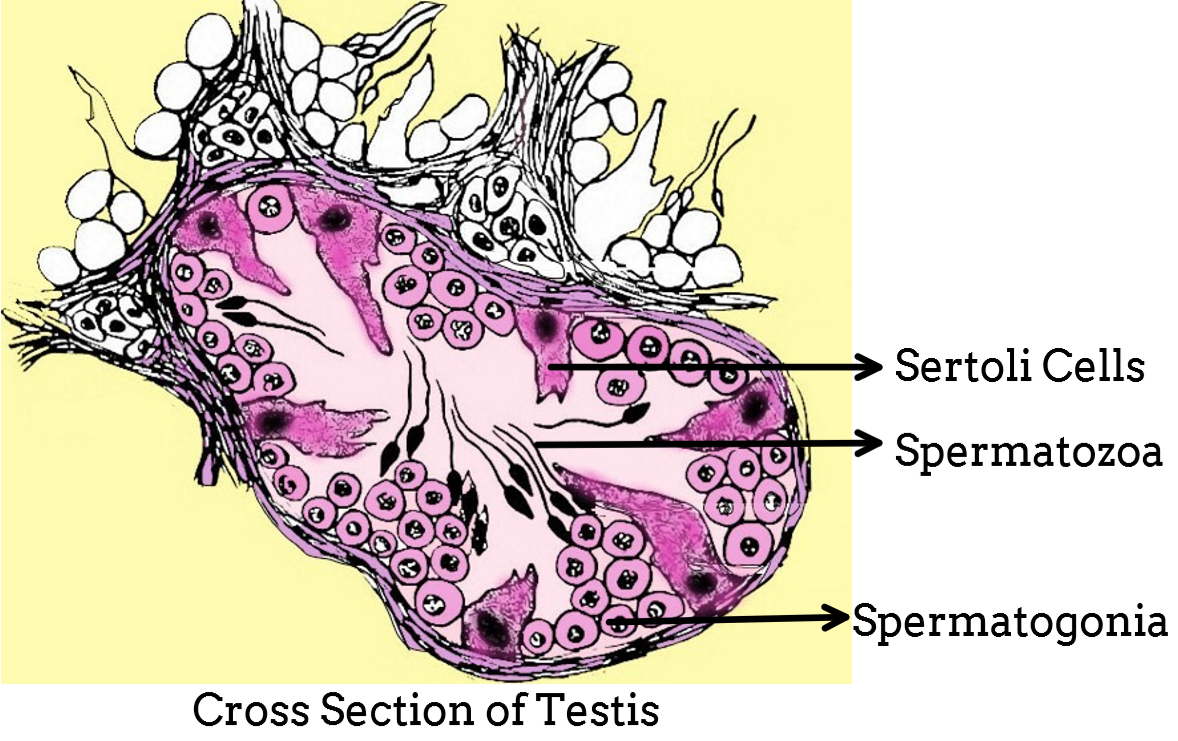
Sertoli cells are also called ‘nurse cells' or ‘mother cells' of the testicle. It is the part of a seminiferous tubule and it helps in the process of spermatogenesis i.e. the production of sperms. Leydig cells are also named as interstitial cells of Leydig. They are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle. Leydig cells are polyhedral in shape, they have a large prominent nucleus and an eosinophilic cytoplasm. They also have numerous lipid-filled vesicles.
Main functions of Sertoli cells are-
-It provides nourishment to the developing sperm cells during spermatogenesis therefore, the Sertoli cells are also named as ‘mother or nurse cell'.
-Sertoli cells also act as phagocytes and consume the residual cytoplasm left during spermatogenesis.
-Sertoli cells secrete the hormones inhibin, ABP (Aromatase Binding Protein), and anti-mullerian hormone.
-They together form the ‘blood testis barrier' that stops the flow of unwanted molecules and pathogens through it.
Main functions of Leydig cells are-
-They release certain hormones known as androgens.
-Androgens are steroidal hormones consisting of testosterone, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). The androstenedione and DHEA are actively converted into testosterone by the enzyme desmolase. Androgens play a very important role in development of secondary sexual characters during puberty such as facial hair growth, sexual behavior, libido, etc. The seminiferous tubules form the parenchyma of the testis.
Note: -Inhibin sends negative feedback to the pituitary gland, decreasing the release of FSH and regulates the process of spermatogenesis.
-Aromatase Binding Protein is responsible for the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone.
-The Anti-mullerian hormone results in the regression of the mullerian tube, uterus, and fallopian tube. This helps in the determination of sexes in the young embryo.
Complete Answer:
Sertoli cells are also called ‘nurse cells' or ‘mother cells' of the testicle. It is the part of a seminiferous tubule and it helps in the process of spermatogenesis i.e. the production of sperms. Leydig cells are also named as interstitial cells of Leydig. They are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle. Leydig cells are polyhedral in shape, they have a large prominent nucleus and an eosinophilic cytoplasm. They also have numerous lipid-filled vesicles.
Main functions of Sertoli cells are-
-It provides nourishment to the developing sperm cells during spermatogenesis therefore, the Sertoli cells are also named as ‘mother or nurse cell'.
-Sertoli cells also act as phagocytes and consume the residual cytoplasm left during spermatogenesis.
-Sertoli cells secrete the hormones inhibin, ABP (Aromatase Binding Protein), and anti-mullerian hormone.
-They together form the ‘blood testis barrier' that stops the flow of unwanted molecules and pathogens through it.
Main functions of Leydig cells are-
-They release certain hormones known as androgens.
-Androgens are steroidal hormones consisting of testosterone, androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). The androstenedione and DHEA are actively converted into testosterone by the enzyme desmolase. Androgens play a very important role in development of secondary sexual characters during puberty such as facial hair growth, sexual behavior, libido, etc. The seminiferous tubules form the parenchyma of the testis.

Note: -Inhibin sends negative feedback to the pituitary gland, decreasing the release of FSH and regulates the process of spermatogenesis.
-Aromatase Binding Protein is responsible for the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone.
-The Anti-mullerian hormone results in the regression of the mullerian tube, uterus, and fallopian tube. This helps in the determination of sexes in the young embryo.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




