
What are the organs of locomotion in Annelids?
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Locomotion is a very general term which means the ability of the organism to move from one place to another. Locomotion in annelids is achieved by the part of the body which is segmented and bristle or hair liked structures.
Complete answer:
The annelids are commonly known as the ringed worms or segmented worms. These are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. Locomotion in annelids is achieved by two structures i.e setae and parapodia.
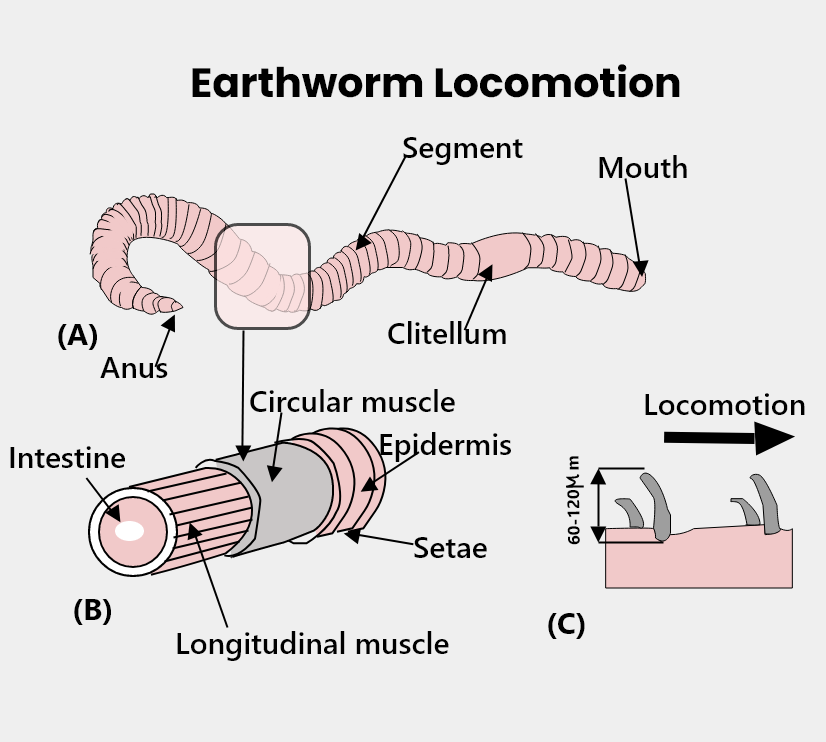
The locomotion in annelids is most studied in earthworms as it is clearly observed in the earthworm because it lacks appendages and parapodia. Movement of earthworms involves extending their body, anchoring it to a surface with the help of setae, and contracting body muscles. When the worm first starts the forward movement, circular muscles at the anterior end contract, extending the head forward. At the same time, the anterior end of the body lifts from the surface to facilitate forward movement. A wavelike contraction originates in the circulatory muscles then passes toward the posterior end. When the wave of contraction comes close to the mid-region of the body, longitudinal muscles contract, thereby shortening the body. A wave of contraction of longitudinal muscles follows, and the cycle is repeated every time until the movement is on. The setae of a segment is extended by the help of certain body muscles to prevent backward movement of the segment during the contraction process of the longitudinal muscles. The setae have to be retracted during the circular contraction period. The earthworm is capable of reversing the direction of its movement, during this time the waves of contraction pass forward.
Note: Most species of the polychaete annelids have a distinct structure for locomotion which is the fleshy parapodia which are segmentally arranged along the body axis. The parapodia varies from organism to organism greatly in size and it’s formed and performs a variety of functions, which are like a gas exchange, anchorage, protection, and locomotion.
Complete answer:
The annelids are commonly known as the ringed worms or segmented worms. These are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. Locomotion in annelids is achieved by two structures i.e setae and parapodia.
The locomotion in annelids is most studied in earthworms as it is clearly observed in the earthworm because it lacks appendages and parapodia. Movement of earthworms involves extending their body, anchoring it to a surface with the help of setae, and contracting body muscles. When the worm first starts the forward movement, circular muscles at the anterior end contract, extending the head forward. At the same time, the anterior end of the body lifts from the surface to facilitate forward movement. A wavelike contraction originates in the circulatory muscles then passes toward the posterior end. When the wave of contraction comes close to the mid-region of the body, longitudinal muscles contract, thereby shortening the body. A wave of contraction of longitudinal muscles follows, and the cycle is repeated every time until the movement is on. The setae of a segment is extended by the help of certain body muscles to prevent backward movement of the segment during the contraction process of the longitudinal muscles. The setae have to be retracted during the circular contraction period. The earthworm is capable of reversing the direction of its movement, during this time the waves of contraction pass forward.

Note: Most species of the polychaete annelids have a distinct structure for locomotion which is the fleshy parapodia which are segmentally arranged along the body axis. The parapodia varies from organism to organism greatly in size and it’s formed and performs a variety of functions, which are like a gas exchange, anchorage, protection, and locomotion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




