
What are the possible fates of pyruvic acid in the body?
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: Glycolysis is common to both aerobic and anaerobic modes of respiration and is called a common pathway. It is the first stage in the breakdown of glucose and is common to all organisms. It occurs in the cytosol and results in the breakdown of glucose or similar hexose sugar into two molecules of a three-carbon compound – pyruvic acid, by releasing some energy and reducing power.
Complete answer:
The important molecule which is present at the intersection of many biochemical pathways is called pyruvate.
Anaerobic respiration -
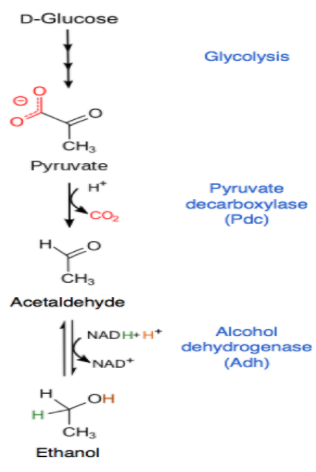
I) Alcoholic Fermentation – It occurs in fungi and bacteria. If the fungus is not in contact with the atmosphere, pyruvate first undergoes decarboxylation with the help of enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase, transacetylase, $Mg^+$ and TPP. With the help of pyruvic acid, this produces acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide.
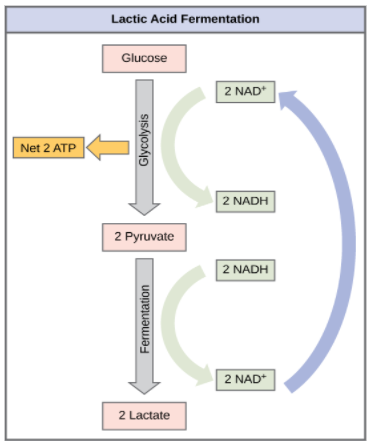
II) Lactic Acid Fermentation – It occurs in lactic acid bacteria and muscles. To form lactic acid Pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is reduced by $NADH_2$.
III) Aerobic Respiration – In aerobic respiration molecular oxygen acts as the ultimate acceptor of electrons and protons removed from the substrate. In the cytosol, pyruvic acid generated is transported to mitochondria, and thus initiates the 2nd phase of respiration. Before pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle, operative in the mitochondria, one of the three carbon atoms of pyruvic acid is oxidized to carbon dioxide in a reaction called oxidative decarboxylation.

Note: Both aerobic and anaerobic types of respiration have a common series of initial steps termed glycolysis. Carbohydrates are converted into pyruvic acid through a series of enzymatic reactions during glycolysis. The pyruvic acid thus formed enters mitochondria, where $O_2$ and the necessary enzymes are available, and pyruvic acid is converted into $CO_2$ and $H_2O$. This reaction series is known as the Krebs cycle.
Complete answer:
The important molecule which is present at the intersection of many biochemical pathways is called pyruvate.
Anaerobic respiration -
I) Alcoholic Fermentation – It occurs in fungi and bacteria. If the fungus is not in contact with the atmosphere, pyruvate first undergoes decarboxylation with the help of enzymes pyruvate decarboxylase, transacetylase, $Mg^+$ and TPP. With the help of pyruvic acid, this produces acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide.

II) Lactic Acid Fermentation – It occurs in lactic acid bacteria and muscles. To form lactic acid Pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is reduced by $NADH_2$.

III) Aerobic Respiration – In aerobic respiration molecular oxygen acts as the ultimate acceptor of electrons and protons removed from the substrate. In the cytosol, pyruvic acid generated is transported to mitochondria, and thus initiates the 2nd phase of respiration. Before pyruvic acid enters the Krebs cycle, operative in the mitochondria, one of the three carbon atoms of pyruvic acid is oxidized to carbon dioxide in a reaction called oxidative decarboxylation.

Note: Both aerobic and anaerobic types of respiration have a common series of initial steps termed glycolysis. Carbohydrates are converted into pyruvic acid through a series of enzymatic reactions during glycolysis. The pyruvic acid thus formed enters mitochondria, where $O_2$ and the necessary enzymes are available, and pyruvic acid is converted into $CO_2$ and $H_2O$. This reaction series is known as the Krebs cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




