
What are the properties of the electromagnetic waves?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: The electromagnetic waves transfer energy by matter or by vacuum. Some electromagnetic waves are usually safe; an example is a light that we use to see. Another electromagnetic wave can be hazardous, and care must be taken to avoid exposure to them; for example, X-rays. All electromagnetic waves travel with the speed of light.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Electromagnetic radiation is a kind of energy generated by the flow of electrically energized particles traveling into material or vacuum or by oscillating electric and magnetic disturbance. The electric and the magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other, and the combination of both electric and magnetic oscillating fields creating the disturbance. Electromagnetic fields provide electromagnetic radiation, also mentioned as EM radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a sort of energy present worldwide and has various types like microwaves, radio waves, X-rays, gamma rays, etc.
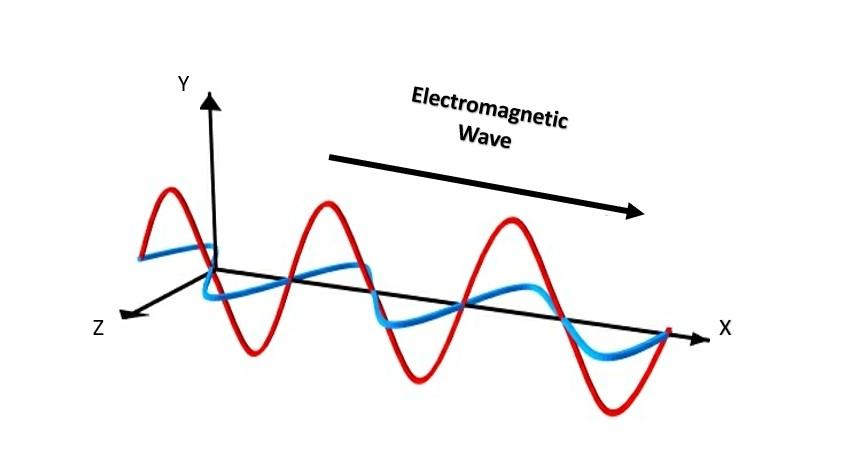
All electromagnetic waves move at an equal speed in a vacuum, i.e., the speed of light $3 \times 10^{8} m s^{-1}$. Nothingness can travel faster than this speed in the universe. The sun is $150$ million kilometers far away from Earth, but it observes that electromagnetic radiation takes only $8$ minutes to come on Earth from the sun.
Electromagnetic radiation consists of photons, these are packets of light energy or quantized harmonious waves that move with the light speed. They can move through space. Waves different from electromagnetic waves have to travel through some substance. Electromagnetic radiations possess a wide variety of frequencies, wavelengths, and energy levels. The symbol $\lambda$ commonly characterizes the wavelength of electromagnetic waves. It is the distance between the troughs or crests and the cycle numbers per second are the frequency.
Additional Information:- Electromagnetic radiation takes place when an atomic particle is quickened by an electric field, inducing it to accelerate. The product of wavelength and frequency for the electromagnetic wave is constant. The shorter the wavelength, the greater the frequency and vice versa. Energy depends on frequency so, the greater the frequency, the higher the energy.
Note: The force between two charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the particles. An electric field in motion creates a magnetic field. A wire in an electric current creates a magnetic field whose orientation depends on its direction. These magnetic and electric waves go right angles to each other and have features like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Electromagnetic radiation is a kind of energy generated by the flow of electrically energized particles traveling into material or vacuum or by oscillating electric and magnetic disturbance. The electric and the magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other, and the combination of both electric and magnetic oscillating fields creating the disturbance. Electromagnetic fields provide electromagnetic radiation, also mentioned as EM radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a sort of energy present worldwide and has various types like microwaves, radio waves, X-rays, gamma rays, etc.

All electromagnetic waves move at an equal speed in a vacuum, i.e., the speed of light $3 \times 10^{8} m s^{-1}$. Nothingness can travel faster than this speed in the universe. The sun is $150$ million kilometers far away from Earth, but it observes that electromagnetic radiation takes only $8$ minutes to come on Earth from the sun.
Electromagnetic radiation consists of photons, these are packets of light energy or quantized harmonious waves that move with the light speed. They can move through space. Waves different from electromagnetic waves have to travel through some substance. Electromagnetic radiations possess a wide variety of frequencies, wavelengths, and energy levels. The symbol $\lambda$ commonly characterizes the wavelength of electromagnetic waves. It is the distance between the troughs or crests and the cycle numbers per second are the frequency.
Additional Information:- Electromagnetic radiation takes place when an atomic particle is quickened by an electric field, inducing it to accelerate. The product of wavelength and frequency for the electromagnetic wave is constant. The shorter the wavelength, the greater the frequency and vice versa. Energy depends on frequency so, the greater the frequency, the higher the energy.
Note: The force between two charges is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the particles. An electric field in motion creates a magnetic field. A wire in an electric current creates a magnetic field whose orientation depends on its direction. These magnetic and electric waves go right angles to each other and have features like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




