
What are the three types of RNAs?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: RNA stands for Ribosomal Nucleic acid. It is one of the major components of the cell that functions in commanding the functioning. Each of the RNA plays a major role in cells from transcription to translation of proteins.
Complete answer:
1. The first type of RNA is mRNA. It stands for messenger RNA. In the process of transcription, the linear molecule strand transcribed from one strand of DNA is called mRNA. It consists of complementary bases to that of the DNA strand from which it is transcribed. It has the base sequence encoded on it in the form of triplet codons. In the translation process, the ribosomes read these codons and form amino acid peptide chains termed as proteins.
2. The second type of RNA is tRNA or transfer RNA. It has a cloverleaf shape. It functions to decode the information present on mRNA in the form of triplet codons. As each triplet codon on mRNA represents an amino acid, the tRNA by acting as an adaptor for mRNA matches the codons over its particular amino acid. It holds mRNA by its trinucleotide sequence called anticodon as the codon on mRNA binds to their complementary sequence called the anticodon.
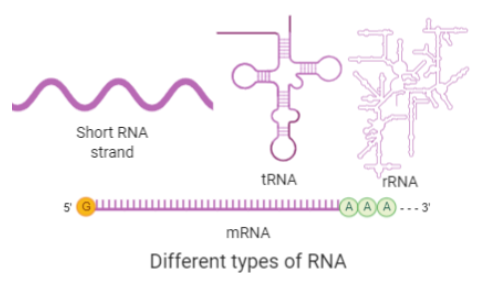
3. The third important type of RNA is rRNA or ribosomal RNA. Now, this RNA plays a major role in protein synthesis. The rRNA molecules by extensive complementary base pairings form secondary structure double-stranded stems and single-stranded loops. The rRNA forms the major units of ribosomes. Ribosomes bind to both the tRNA and mRNA to bring them together to begin the process of translation.
Note: The rRNA is the predominant molecule found in a cell out of the three RNA types. It constitutes about $85%$ of total RNA. The rRNAs can exist in many forms in the ribosomes. In some cases, the RNA is also present in the form of enzymes and these are called ribozymes.
Complete answer:
1. The first type of RNA is mRNA. It stands for messenger RNA. In the process of transcription, the linear molecule strand transcribed from one strand of DNA is called mRNA. It consists of complementary bases to that of the DNA strand from which it is transcribed. It has the base sequence encoded on it in the form of triplet codons. In the translation process, the ribosomes read these codons and form amino acid peptide chains termed as proteins.
2. The second type of RNA is tRNA or transfer RNA. It has a cloverleaf shape. It functions to decode the information present on mRNA in the form of triplet codons. As each triplet codon on mRNA represents an amino acid, the tRNA by acting as an adaptor for mRNA matches the codons over its particular amino acid. It holds mRNA by its trinucleotide sequence called anticodon as the codon on mRNA binds to their complementary sequence called the anticodon.

3. The third important type of RNA is rRNA or ribosomal RNA. Now, this RNA plays a major role in protein synthesis. The rRNA molecules by extensive complementary base pairings form secondary structure double-stranded stems and single-stranded loops. The rRNA forms the major units of ribosomes. Ribosomes bind to both the tRNA and mRNA to bring them together to begin the process of translation.
Note: The rRNA is the predominant molecule found in a cell out of the three RNA types. It constitutes about $85%$ of total RNA. The rRNAs can exist in many forms in the ribosomes. In some cases, the RNA is also present in the form of enzymes and these are called ribozymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




