
What are the two types of arrangement in plastics?
A. Linear, Horizontal
B. Horizontal, Cross-linked
C. Linear, Cross-linked
D. Linear, Vertical
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Plastic is a type of polymer that may be recycled, coloured, reused, moulded, and formed into wires and other shapes. Some plastics have a linear organisation of their units, whereas others have a cross connected layout of their units.
Complete answer:
Plastic is any organic polymer that is synthetic or semi-synthetic. In other words, while additional elements may be present, carbon and hydrogen are always present in plastics. While plastics can be manufactured from almost any organic polymer, petrochemicals are used to make the majority of industrial plastics.
Colorants, plasticizers, stabilisers, fillers, and reinforcements are virtually always included into the polymer used to produce plastic. Plastic's chemical composition, chemical properties, and mechanical capabilities, as well as its cost, are all affected by these additives.
These units of plastic polymer can be organised in a linear or cross-linked pattern.
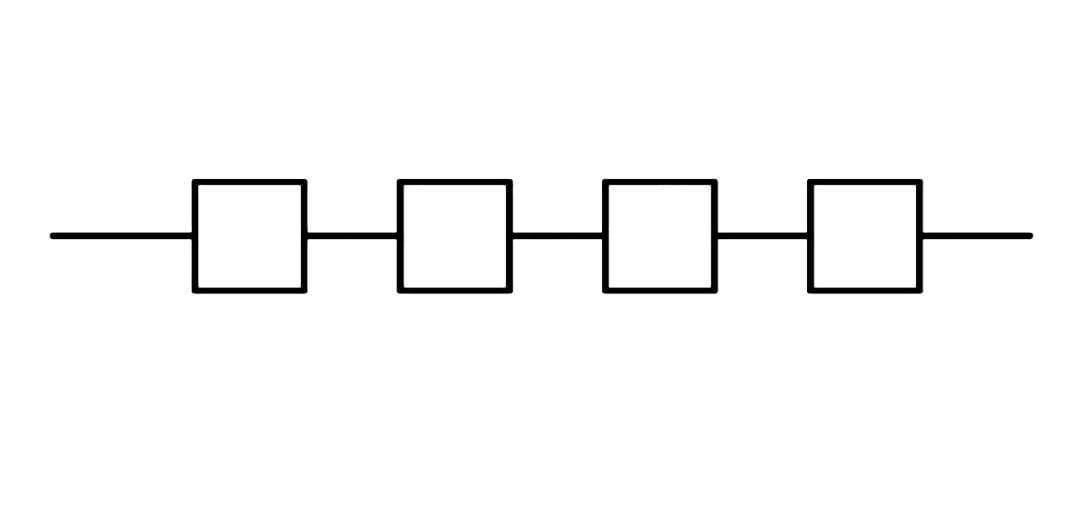
As seen in the diagram above, linear polymers are ones in which the polymer chains do not contain long-chain branching.

As illustrated in the diagram, plastic polymer can also be classed as a branch polymer.
Cross-linked polymers, on the other hand, have chemical linkages created between adjacent polymer chains, resulting in a network structure.
So, the correct option is: (C) Linear, Cross-linked.
Note:
Plastics are polymers, but polymers are not always plastics. Monomers are chains of connected subunits that make up plastic polymers. A homopolymer is formed when identical monomers are linked together. Copolymers are made up of different monomers linked together. Straight or branched chains can be found in homopolymers and copolymers.
Complete answer:
Plastic is any organic polymer that is synthetic or semi-synthetic. In other words, while additional elements may be present, carbon and hydrogen are always present in plastics. While plastics can be manufactured from almost any organic polymer, petrochemicals are used to make the majority of industrial plastics.
Colorants, plasticizers, stabilisers, fillers, and reinforcements are virtually always included into the polymer used to produce plastic. Plastic's chemical composition, chemical properties, and mechanical capabilities, as well as its cost, are all affected by these additives.
These units of plastic polymer can be organised in a linear or cross-linked pattern.

As seen in the diagram above, linear polymers are ones in which the polymer chains do not contain long-chain branching.

As illustrated in the diagram, plastic polymer can also be classed as a branch polymer.
Cross-linked polymers, on the other hand, have chemical linkages created between adjacent polymer chains, resulting in a network structure.
So, the correct option is: (C) Linear, Cross-linked.
Note:
Plastics are polymers, but polymers are not always plastics. Monomers are chains of connected subunits that make up plastic polymers. A homopolymer is formed when identical monomers are linked together. Copolymers are made up of different monomers linked together. Straight or branched chains can be found in homopolymers and copolymers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




