
What are the types of wavefront?
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: Wave front is an imaginary field that shows the points where all the waves present at that point have the same phase. Wavefronts vary according to their source points. Different source points have different types of wavefront. Wavefronts are completely imaginary fields just like the field lines we studied in electromagnetism.
Complete answer:
Wavefronts are classified in three types. Each type of wavefront depends on their source. The three types of wavefronts are as follows-
Spherical wavefront:
This type of wavefront is produced by point source objects or we can say that we observe this type of wavefront by point sources. As the name denotes, these wavefronts are spherical in shape. An illustration for this type of wavefront is as follows.
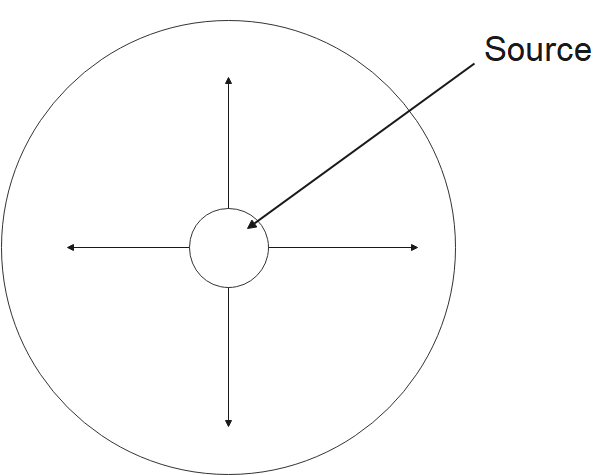
Cylindrical Wavefront:
This type of wavefront is formed when the source of light is linear in shape and hence when the light waves travel in all possible directions it makes a cylindrical shape and hence this is the reason that this type of wavefront is known as cylindrical wavefront.
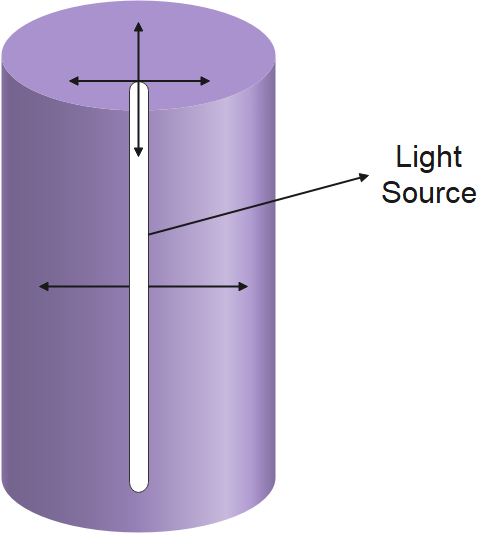
Plane Wavefront:
This type of wavefront is formed when we observe the light rays coming from a very distant object, we can assume the source of light as infinity as it is very far away from the observed and hence when we observe the rays, we observe a little area of it which seems like a 2D plane and hence this is known as plane wavefront.
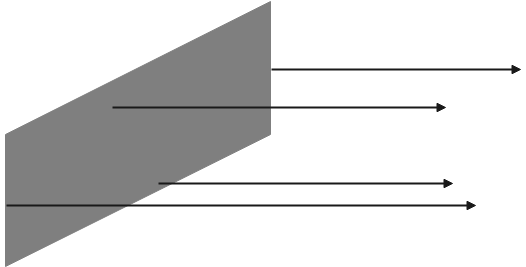
Note:
Wavefront is used to determine the route of the waves and it is helpful as the phase is the same for all the waves at a given point in a wavefront. Wavefronts are the same as field lines in our electromagnetism. Both field lines and wavefronts are imaginary and they are used to determine the effect felt in a given particular area to minimize and make our calculations easy.
Complete answer:
Wavefronts are classified in three types. Each type of wavefront depends on their source. The three types of wavefronts are as follows-
Spherical wavefront:
This type of wavefront is produced by point source objects or we can say that we observe this type of wavefront by point sources. As the name denotes, these wavefronts are spherical in shape. An illustration for this type of wavefront is as follows.

Cylindrical Wavefront:
This type of wavefront is formed when the source of light is linear in shape and hence when the light waves travel in all possible directions it makes a cylindrical shape and hence this is the reason that this type of wavefront is known as cylindrical wavefront.

Plane Wavefront:
This type of wavefront is formed when we observe the light rays coming from a very distant object, we can assume the source of light as infinity as it is very far away from the observed and hence when we observe the rays, we observe a little area of it which seems like a 2D plane and hence this is known as plane wavefront.

Note:
Wavefront is used to determine the route of the waves and it is helpful as the phase is the same for all the waves at a given point in a wavefront. Wavefronts are the same as field lines in our electromagnetism. Both field lines and wavefronts are imaginary and they are used to determine the effect felt in a given particular area to minimize and make our calculations easy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




