
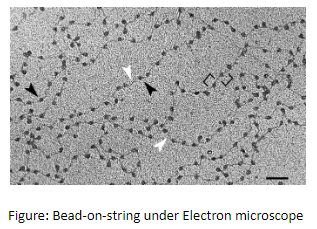
What are those structures that appear as “beads-on-string” in the chromosomes, when viewed under an electron microscope?
A) Base pairs
B) Genes
C) Nucleotides
D) Nucleosomes
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: The chromatin fibres are formed when the beads-on-string structure in chromatin is packaged. These chromatin fibres further coil and condensed in cell division (metaphase stage) to form chromosomes.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The packaging of DNA helix in eukaryotes is more complex as compared to prokaryotes. There is a set of a positively charged protein called histones. These charges are depending upon the abundance of amino acids residues with charged side chains. The histones are rich arginines and lysines amino acid residues. These amino acid residues carry a positive charge in their side chain. Histones are arranged to form a unit of eight molecules, called histone octamers. The DNA that is negatively charged is wrapped around a histone octamer (positively charged) and forms a structure called a nucleosome. A classic nucleosome contains 200bp of DNA helix. In the nucleus, the nucleosome constitutes the repeating unit of a structure called chromatin. It is a thread-like stained body present in the nucleus. When viewed under electron microscopes the nucleosome in chromatin appeared as a bead-on-string structure. The bead-on-string is packed in the chromatin and forms the chromatin fibres. Further, these fibres condensed and coiled in the metaphase stage of the cell division to form chromosomes. At a higher level, the packaging of chromatin required an additional set of a protein called non-histone chromosomal protein.
Option D is the correct answer.
Note: In prokaryotes such as E.coli, they do have a defined nucleus. Hence the DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. The region called a nucleoid, the negatively charged DNA is held by some positively charged protein. The DNA in the nucleoid is arranged in a large loop held by protein.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The packaging of DNA helix in eukaryotes is more complex as compared to prokaryotes. There is a set of a positively charged protein called histones. These charges are depending upon the abundance of amino acids residues with charged side chains. The histones are rich arginines and lysines amino acid residues. These amino acid residues carry a positive charge in their side chain. Histones are arranged to form a unit of eight molecules, called histone octamers. The DNA that is negatively charged is wrapped around a histone octamer (positively charged) and forms a structure called a nucleosome. A classic nucleosome contains 200bp of DNA helix. In the nucleus, the nucleosome constitutes the repeating unit of a structure called chromatin. It is a thread-like stained body present in the nucleus. When viewed under electron microscopes the nucleosome in chromatin appeared as a bead-on-string structure. The bead-on-string is packed in the chromatin and forms the chromatin fibres. Further, these fibres condensed and coiled in the metaphase stage of the cell division to form chromosomes. At a higher level, the packaging of chromatin required an additional set of a protein called non-histone chromosomal protein.

Option D is the correct answer.
Note: In prokaryotes such as E.coli, they do have a defined nucleus. Hence the DNA is not scattered throughout the cell. The region called a nucleoid, the negatively charged DNA is held by some positively charged protein. The DNA in the nucleoid is arranged in a large loop held by protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




