
What are two types of ribosomes, what does each do?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: Ribosomes are the integral part of the cell. The ribosomes are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. The role of the ribosome in the cell is they are the site of protein synthesis.
Complete answer:
Protein synthesis is the most important and integral need of the cell. All the cells may it be prokaryotic or eukaryotic have ribosomes. The ribosomes are the entre where the mRNA translates into protein. The ribosomes are scattered in the cytoplasm and are not bounded by a complex membrane. The ribosomes are made up of RNA and proteins. The ribosomes are made up of two subunits- a smaller unit which is the site for mRNA to bind and the larger unit where the amino acid is added.
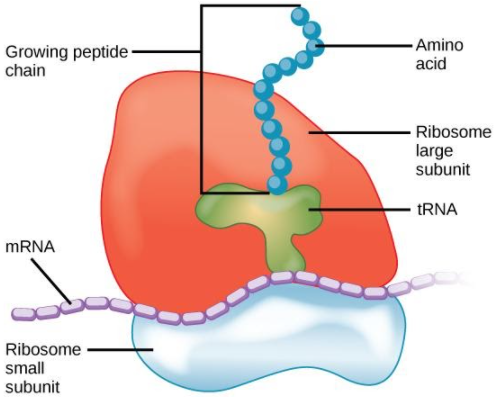
Depending on the type of cell, the ribosomes are of two types-
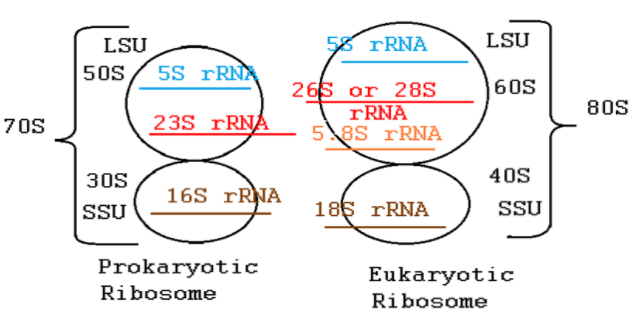
i) 70S ribosome- This type of ribosome is present in the prokaryotes like bacteria and archaebacteria. It is composed of two subunits 30S and 50S. These are smaller in length and diameter. The sedimentation coefficient of this type is 70. They contain around 8000 amino acid and 55 proteins. They contain 3 molecules of RNA. The function of the 70S ribosome is to synthesise the necessary proteins for the functioning of the prokaryotic cell.
ii) 80S ribosome- This type of ribosome is the characteristic of the eukaryotic cell. They are found either freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The sedimentation coefficient of the 80S is 80. They contain 4 molecules of RNA. They contain around 80 proteins. The two subunits of the 80S are 60S and 40S.
The function of the ribosome:
- Translates the information from the nucleus in the form of mRNA into amino acid
- Link the amino acids together by forming a peptide bond.
Note: Photosynthesis is one of the essential processes which directly influences life on earth. The product obtained as a result of photosynthesis is directly and indirectly consumed by all the living forms. It converts solar energy into chemical energy.
Complete answer:
Protein synthesis is the most important and integral need of the cell. All the cells may it be prokaryotic or eukaryotic have ribosomes. The ribosomes are the entre where the mRNA translates into protein. The ribosomes are scattered in the cytoplasm and are not bounded by a complex membrane. The ribosomes are made up of RNA and proteins. The ribosomes are made up of two subunits- a smaller unit which is the site for mRNA to bind and the larger unit where the amino acid is added.

Depending on the type of cell, the ribosomes are of two types-
i) 70S ribosome- This type of ribosome is present in the prokaryotes like bacteria and archaebacteria. It is composed of two subunits 30S and 50S. These are smaller in length and diameter. The sedimentation coefficient of this type is 70. They contain around 8000 amino acid and 55 proteins. They contain 3 molecules of RNA. The function of the 70S ribosome is to synthesise the necessary proteins for the functioning of the prokaryotic cell.
ii) 80S ribosome- This type of ribosome is the characteristic of the eukaryotic cell. They are found either freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The sedimentation coefficient of the 80S is 80. They contain 4 molecules of RNA. They contain around 80 proteins. The two subunits of the 80S are 60S and 40S.

The function of the ribosome:
- Translates the information from the nucleus in the form of mRNA into amino acid
- Link the amino acids together by forming a peptide bond.
Note: Photosynthesis is one of the essential processes which directly influences life on earth. The product obtained as a result of photosynthesis is directly and indirectly consumed by all the living forms. It converts solar energy into chemical energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




