
Area of parallelogram formed by the lines \[y = mx,y = mx + 1,y = nx\] and \[y = nx + 1\] equals to
A. \[\dfrac{{\left| {m + n} \right|}}{{{{\left( {m - n} \right)}^2}}}\]
B. \[\dfrac{2}{{\left| {m + n} \right|}}\]
C. \[\dfrac{1}{{\left| {m + n} \right|}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{1}{{\left| {m - n} \right|}}\]
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: In order to find the area of parallelogram first make the graph by the given lines then find the coordinates of the parallelogram and by using the formula of area of triangle which is given below we will proceed further.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given lines are \[y = mx,y = mx + 1,y = nx\] and \[y = nx + 1\]. So, first we will make a graph as shown in the below:
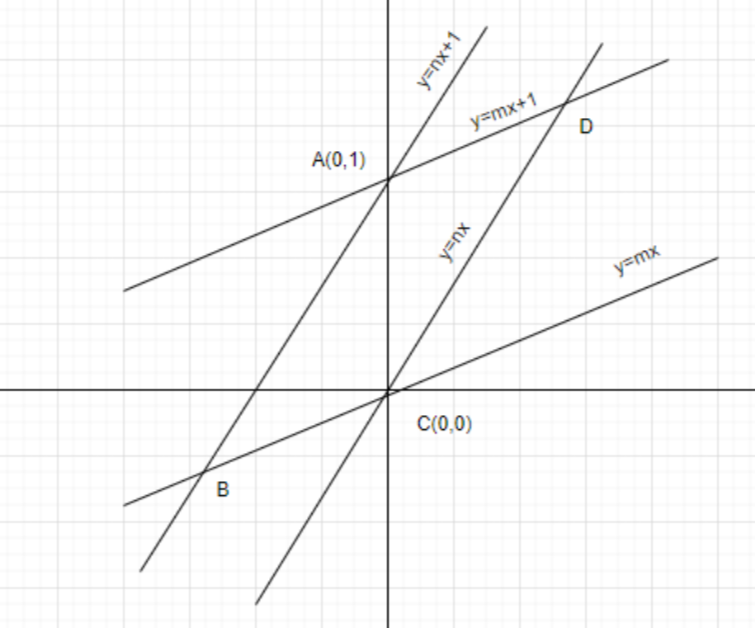
From figure we get the parallelogram ABCD, now we will find out its coordinate
Here \[A\left( {0,1} \right)\] and \[C\left( {0,0} \right)\]
For point B: The lines \[y = mx\] and \[y = nx + 1\] intersect each other at a point B
So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow mx = nx + 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{{m - n}} \\
\]
Substitute this value in the line \[y = mx\], then we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{m}{{m - n}}\]
So, the coordinate of B is \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right)\]
For D point: The two lines \[y = nx\] and \[y = mx + 1\] intersects at a point D. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow nx = mx + 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{{n - m}} \\
\]
By substituting this value in the line \[y = nx\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{n}{{n - m}}\]
So, the coordinate D is \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{{n - m}},\dfrac{n}{{n - m}}} \right)\]
Therefore, coordinates of parallelogram ABCD are \[A\left( {0,1} \right),B\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right),C\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[D\left( {\dfrac{1}{{n - m}},\dfrac{n}{{n - m}}} \right)\].
From the figure we have seen that area of parallelogram ABCD = \[2 \times {\text{Area of }}\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]
We know that the area of \[\Delta PQR\] where, \[P\left( {{x_1},{y_2}} \right),Q\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] and \[R\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is
\[\Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
So, area of \[\Delta {\text{ABC}}\] with \[A\left( {0,1} \right),B\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right),C\left( {0,0} \right)\] is
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
0&1&1 \\
{\dfrac{1}{{m - n}}}&{\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}}&1 \\
0&0&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
Opening the determinant, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\left[ {0 - \dfrac{1}{{m - n}} + 0} \right]} \right| \\
\therefore \Delta = \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}} \\
\]
Therefore, area of \[\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}}\]
Hence, area of parallelogram ABCD =\[2 \times {\text{Area of }}\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]= \[2 \times \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}}\] = \[\dfrac{1}{{\left| {m - n} \right|}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Students must remember the formula for finding the area of the triangle by determinant method. The determinant method is very handy to find the area of figure in coordinate geometry. The determinant is a scalar value that can be computed from the elements of a square matrix and encodes certain properties of the linear transformation described by the matrix. The determinant of a matrix A is denoted det A.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given lines are \[y = mx,y = mx + 1,y = nx\] and \[y = nx + 1\]. So, first we will make a graph as shown in the below:

From figure we get the parallelogram ABCD, now we will find out its coordinate
Here \[A\left( {0,1} \right)\] and \[C\left( {0,0} \right)\]
For point B: The lines \[y = mx\] and \[y = nx + 1\] intersect each other at a point B
So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow mx = nx + 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{{m - n}} \\
\]
Substitute this value in the line \[y = mx\], then we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{m}{{m - n}}\]
So, the coordinate of B is \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right)\]
For D point: The two lines \[y = nx\] and \[y = mx + 1\] intersects at a point D. So, we have
\[
\Rightarrow nx = mx + 1 \\
\Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{{n - m}} \\
\]
By substituting this value in the line \[y = nx\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{n}{{n - m}}\]
So, the coordinate D is \[\left( {\dfrac{1}{{n - m}},\dfrac{n}{{n - m}}} \right)\]
Therefore, coordinates of parallelogram ABCD are \[A\left( {0,1} \right),B\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right),C\left( {0,0} \right)\] and \[D\left( {\dfrac{1}{{n - m}},\dfrac{n}{{n - m}}} \right)\].
From the figure we have seen that area of parallelogram ABCD = \[2 \times {\text{Area of }}\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]
We know that the area of \[\Delta PQR\] where, \[P\left( {{x_1},{y_2}} \right),Q\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] and \[R\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is
\[\Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
So, area of \[\Delta {\text{ABC}}\] with \[A\left( {0,1} \right),B\left( {\dfrac{1}{{m - n}},\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}} \right),C\left( {0,0} \right)\] is
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
0&1&1 \\
{\dfrac{1}{{m - n}}}&{\dfrac{m}{{m - n}}}&1 \\
0&0&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
Opening the determinant, we have
\[
\Rightarrow \Delta = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\left[ {0 - \dfrac{1}{{m - n}} + 0} \right]} \right| \\
\therefore \Delta = \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}} \\
\]
Therefore, area of \[\Delta ABC = \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}}\]
Hence, area of parallelogram ABCD =\[2 \times {\text{Area of }}\Delta {\text{ABC}}\]= \[2 \times \dfrac{1}{{2\left| {m - n} \right|}}\] = \[\dfrac{1}{{\left| {m - n} \right|}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Students must remember the formula for finding the area of the triangle by determinant method. The determinant method is very handy to find the area of figure in coordinate geometry. The determinant is a scalar value that can be computed from the elements of a square matrix and encodes certain properties of the linear transformation described by the matrix. The determinant of a matrix A is denoted det A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




