
Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their reactivity towards HCN.
I. Acetaldehyde
II. Acetone
III. Methyl-tert-butyl ketone
IV. Di-tert-butyl ketone
A. $\text{III}<\text{II}<\text{IV}<\text{I}$
B. $\text{II}<\text{I}<\text{IV}<\text{III}$
C. $\text{IV}<\text{III}<\text{II}<\text{I}$
D. $\text{II}<\text{IV}<\text{I}<\text{III}$
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Acetaldehyde comes under aldehydes. Aldehydes contain a functional group with the structure $-\text{CHO}$, where one left valency of carbon is attached to some R groups which can be alkyl or side chain. Ketone is a functional group in organic chemistry containing a carbonyl group. Acetone, methyl-tert-butyl ketone and di-tert-butyl ketone comes under ketones. Addition of HCN is a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, HCN is added to carbonyl groups, such reactions are called nucleophilic addition reactions, so reactivity will also be judged on the basis of addition of nucleophiles. Let us discuss the reactivity order of the given compounds, reactivity between aldehydes and ketones is decided by two factors: (1) Steric hindrance (2) Electrophilicity of carbon
(1) Steric hindrance: It is the congestion caused by the presence of surrounding atoms which may slow down or even prevent reaction to occur. In ketones, there is large hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups attached to $\text{C=O}$: due to which the incoming nucleophile does not find the space to form bonds with carbon. Hence, ketones are less reactive than aldehydes.
(2) Electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon: Due to electronegativity of oxygen the double-bonded carbon attached to it acquires partial positive charge, which makes the attack of nucleophiles easier. But the presence of electron donating groups nullifies the positive charge created. Thus, the presence of electron donating groups decreases the nucleophilic addition reaction.
Let us now compare all four compounds on the basis of these factors:
This is clear that acetaldehyde is most reactive towards HCN addition as it is electrophilic and most important it is least hindered by groups. The reaction between ethanal and HCN will be
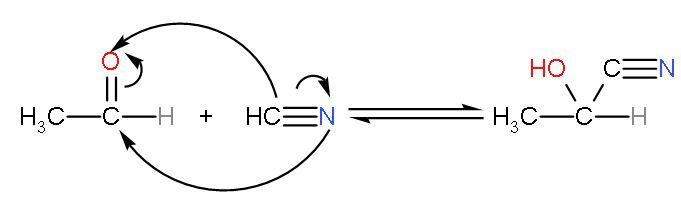
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The point to note in this nucleophilic addition reaction is that addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds is a reversible reaction. The reactant and product exist in equilibrium state with each other. The products formed are cyanohydrins or hydroxy alkane nitrile.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, HCN is added to carbonyl groups, such reactions are called nucleophilic addition reactions, so reactivity will also be judged on the basis of addition of nucleophiles. Let us discuss the reactivity order of the given compounds, reactivity between aldehydes and ketones is decided by two factors: (1) Steric hindrance (2) Electrophilicity of carbon
(1) Steric hindrance: It is the congestion caused by the presence of surrounding atoms which may slow down or even prevent reaction to occur. In ketones, there is large hindrance caused by the bulky alkyl groups attached to $\text{C=O}$: due to which the incoming nucleophile does not find the space to form bonds with carbon. Hence, ketones are less reactive than aldehydes.
(2) Electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon: Due to electronegativity of oxygen the double-bonded carbon attached to it acquires partial positive charge, which makes the attack of nucleophiles easier. But the presence of electron donating groups nullifies the positive charge created. Thus, the presence of electron donating groups decreases the nucleophilic addition reaction.
Let us now compare all four compounds on the basis of these factors:
| S. No. | Name of compounds | Structures of compounds | Whether aldehydes or ketones | Steric hindrance | Electrophilicity |
| I. | Acetaldehyde | 
| Have $-\text{CHO}$ group attached. So, it is aldehyde. | Have hindrance caused by methyl groups only on one side. | This compound is electrophilic caused by methyl group and hydrogen atom. |
| II. | Acetone | 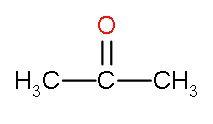
| It is ketone as both the valencies are filled by methyl groups. | Both the methyl groups have caused hindrance at both the sides. | This compound is very less electrophilic because of the positive inductive effect caused by two methyl groups. |
| III. | Methyl-tert-butyl ketone | 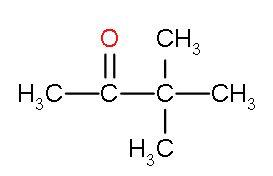
| It is a ketone as suggested by the name. | This compound is highly hindered by tert-butyl group as it has three bulky methyl groups attached and less hindrance at other side. | The electrophilicity is caused by tert-butyl group but electron donation is done by methyl group. So, it is less electrophilic. |
| IV. | Di-tert-butyl ketone | 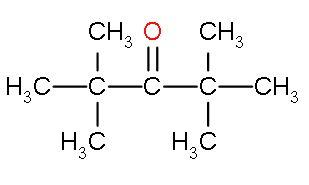
| It also comes under ketones. | This compound is highly hindered by tert-butyl group at both sides as it has three bulky methyl groups attached. There is no space for a nucleophile to enter. | This is highly electrophilic as methyl groups will show positive inductive effect to carbons next to the carbonyl group and negative charge is present on the carbonyl group. Also there is electron deficiency due to oxygen atom also. |
This is clear that acetaldehyde is most reactive towards HCN addition as it is electrophilic and most important it is least hindered by groups. The reaction between ethanal and HCN will be

So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: The point to note in this nucleophilic addition reaction is that addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds is a reversible reaction. The reactant and product exist in equilibrium state with each other. The products formed are cyanohydrins or hydroxy alkane nitrile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




