
Arrange the layer of ovum in chronological order from inside to outside
A. Zona pellucida, vitelline membrane and Corona radiata
B. Corona radiata, Zona pellucida and vitelline membrane
C. Corona radiata, Vitelline membrane and zona pellucida
D. Vitelline membrane, Zona pellucida and Corona radiata
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: After ovulation the newly formed egg is covered by the layer of corona radiata. After ovulation, the egg released includes a secondary oocyte and the first polar body, produced as meiosis I separates the primary oocyte.
Complete Answer:
- The ovaries are tiny, oval-shaped glands at either side of the uterus.
- Eggs and hormones are formed in ovaries. The egg cells are formed by the ovaries, named the ova or oocytes.
- The oocytes are then transferred to the Fallopian tube where a sperm will fertilize. The fertilized egg then travels to the uterus, where in addition to the usual menstrual cycle hormones the uterine lining has thickened.
Now, let us find the solution from the option.
- The vitelline membrane is a framework covering the outer surface of an ovum's plasma membrane (the oolemma), or the extracellular yolk and oolemma in certain organisms ( e.g., birds).
- The zona pellucida is a layer of glycoprotein covering the mammalian oocyte plasma membrane.
The corona radiata is the inner part of the cumulus oophorus cells and it is immediately adjacent to the zona pellucida.
-Human ova are exceedingly minute in diameter reaching 0.2 mm and are wrapped within an ovary’s egg follicle.
-An egg consists of a substance known as yolk or ooplasm, the nucleus is known as the germinal centre and nucleolus known as the germinal spot.
-The membrane that creates an ovum's surface layer is named as a vitelline membrane.
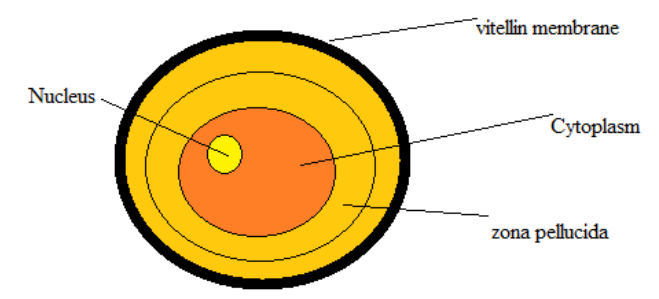
Thus, the correct option is (D) Vitelline membrane, Zona pellucida and Corona radiata.
Note: The female reproductive system increasingly ends up making the female hormones required for the reproductive cycle to function during menopause. Menstrual cycles can become erratic at this stage, and finally stop.
Complete Answer:
- The ovaries are tiny, oval-shaped glands at either side of the uterus.
- Eggs and hormones are formed in ovaries. The egg cells are formed by the ovaries, named the ova or oocytes.
- The oocytes are then transferred to the Fallopian tube where a sperm will fertilize. The fertilized egg then travels to the uterus, where in addition to the usual menstrual cycle hormones the uterine lining has thickened.
Now, let us find the solution from the option.
- The vitelline membrane is a framework covering the outer surface of an ovum's plasma membrane (the oolemma), or the extracellular yolk and oolemma in certain organisms ( e.g., birds).
- The zona pellucida is a layer of glycoprotein covering the mammalian oocyte plasma membrane.
The corona radiata is the inner part of the cumulus oophorus cells and it is immediately adjacent to the zona pellucida.
-Human ova are exceedingly minute in diameter reaching 0.2 mm and are wrapped within an ovary’s egg follicle.
-An egg consists of a substance known as yolk or ooplasm, the nucleus is known as the germinal centre and nucleolus known as the germinal spot.
-The membrane that creates an ovum's surface layer is named as a vitelline membrane.

Thus, the correct option is (D) Vitelline membrane, Zona pellucida and Corona radiata.
Note: The female reproductive system increasingly ends up making the female hormones required for the reproductive cycle to function during menopause. Menstrual cycles can become erratic at this stage, and finally stop.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




