
Derive mirror equation. State any three experimental observations of photoelectric emission.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: In a spherical mirror, the distance of the object from its pole is called the object distance (u). The distance of the image from the pole of the mirror is called the image distance (v). The distance of the principal focus from the pole is called the focal length (f). There is a relationship between these three quantities given by the mirror formula which is expressed as $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$.This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
Derivation of the Mirror Formula
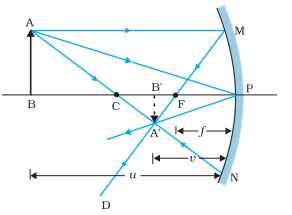
We now derive the mirror equation or the relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f). In the above figure, the two right-angled triangles A′B′F and MPF are similar.
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{PM}} = \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} \\
\because PM = AB...............(1) \\
\Rightarrow \angle APB = \angle {A'}PB \\
\therefore \Delta {A'}{B'}{P'} \sim \Delta A{B'}P \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P}}{{BP}}............(2) \\
By{\text{ }}comparing{\text{ }}equation(1){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}(2),{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P - FP}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P}}{{BP}} \\
\Rightarrow {B'}P = - v,FP = - f,BP = - u \\
U\sin g{\text{ }}these{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}equation,{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - v + f}}{{ - f}} = \dfrac{{ - v}}{{ - u}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{v - f}}{f} = \dfrac{v}{u} \\
On{\text{ }}further{\text{ }}solving,{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\therefore \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \\
$
Note: In a spherical mirror, the distance of the object from its pole is called the object distance (u). The distance of the image from the pole of the mirror is called the image distance (v). The distance of the principal focus from the pole is called the focal length (f). There is a relationship between these three quantities given by the mirror formula which is expressed as $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$.This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object.
Complete step by step solution:
Derivation of the Mirror Formula

We now derive the mirror equation or the relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and the focal length (f). In the above figure, the two right-angled triangles A′B′F and MPF are similar.
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{PM}} = \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} \\
\because PM = AB...............(1) \\
\Rightarrow \angle APB = \angle {A'}PB \\
\therefore \Delta {A'}{B'}{P'} \sim \Delta A{B'}P \\
\therefore \dfrac{{{B'}{A'}}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P}}{{BP}}............(2) \\
By{\text{ }}comparing{\text{ }}equation(1){\text{ }}and{\text{ }}(2),{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{B'}F}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P - FP}}{{FP}} = \dfrac{{{B'}P}}{{BP}} \\
\Rightarrow {B'}P = - v,FP = - f,BP = - u \\
U\sin g{\text{ }}these{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}equation,{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - v + f}}{{ - f}} = \dfrac{{ - v}}{{ - u}} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{v - f}}{f} = \dfrac{v}{u} \\
On{\text{ }}further{\text{ }}solving,{\text{ }}we{\text{ }}get \\
\therefore \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} \\
$
Note: In a spherical mirror, the distance of the object from its pole is called the object distance (u). The distance of the image from the pole of the mirror is called the image distance (v). The distance of the principal focus from the pole is called the focal length (f). There is a relationship between these three quantities given by the mirror formula which is expressed as $\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$.This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




