
Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to:
A) The formation of less stable carbonium ions.
B) Resonance stabilization.
C) Larger carbon-halogen bond.
D) Inductive effect.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this we must know the difference in aryl halides and alkyl halides. Aryl halides are aromatic compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of the aromatic ring are replaced by a halogen. Alkyl halides are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by a halogen.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that aryl halides are aromatic compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of the aromatic ring is replaced by a halogen. And alkyl halides are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by a halogen.
The structures of aryl halide and alkyl halide are as follows:
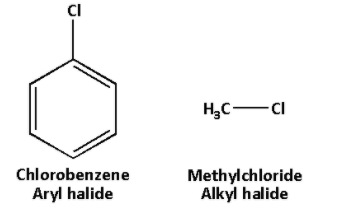
In aryl halides, there is presence of resonance. But in alkyl halides, resonance is absent.
In aryl halides, the bond between carbon and chlorine $\left( {{\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}} \right)$ acquires a partial double bond character. Due to this the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond becomes shorter and stronger. As the bond becomes stronger it is difficult to break the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond.
As a result aryl halides become less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The resonance in aryl halide is as follows:
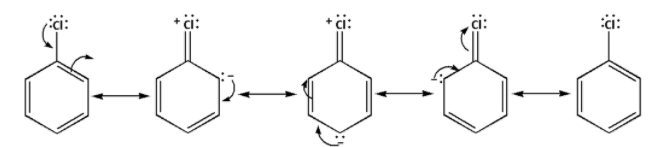
The resonance is absent in alkyl halides and thus, alkyl halides are more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Thus, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to resonance stabilization.
Thus, the correct answer is option (B) resonance stabilization.
Note: The reaction in which one nucleophile is replaced by another nucleophile is known as a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The group which takes the electron pair with it and gets displaced from the carbon is known as the leaving group. The leaving group leaves as an anion or as a neutral molecule leaving behind a carbonium ion.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know that aryl halides are aromatic compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms of the aromatic ring is replaced by a halogen. And alkyl halides are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by a halogen.
The structures of aryl halide and alkyl halide are as follows:

In aryl halides, there is presence of resonance. But in alkyl halides, resonance is absent.
In aryl halides, the bond between carbon and chlorine $\left( {{\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}} \right)$ acquires a partial double bond character. Due to this the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond becomes shorter and stronger. As the bond becomes stronger it is difficult to break the ${\text{C}} - {\text{Cl}}$ bond.
As a result aryl halides become less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The resonance in aryl halide is as follows:

The resonance is absent in alkyl halides and thus, alkyl halides are more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Thus, aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to resonance stabilization.
Thus, the correct answer is option (B) resonance stabilization.
Note: The reaction in which one nucleophile is replaced by another nucleophile is known as a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The group which takes the electron pair with it and gets displaced from the carbon is known as the leaving group. The leaving group leaves as an anion or as a neutral molecule leaving behind a carbonium ion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




