
Assertion: D-glucose is dextrorotatory whereas L-glucose is laevorotatory.
Reason: D-compounds are always dextro and L-compounds are always laevorotatory.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for assertion
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for assertion
(C) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
(D) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we must recall the concepts of optically active compounds. We should also have knowledge about the two different enantiomers of glucose in D-L configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
In a Fischer projection, we see that the L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the penultimate asymmetric carbon and hydrogen on the right, while D isomers have the hydroxyl group on the right side. This assignment of D and L is used to distinguish between two molecules that are enantiomers that should mean they have a relationship on the basis of reflection; with one molecule being a mirror image of the other.
On the other hand, dextrorotation and levorotation simply refers to the rotation of an optically active compound by a plane polarized light. From the point of view of the observer, a dextrorotatory compound rotates the light clockwise towards the right side whereas a levorotatory compound rotates in anticlockwise towards the left side.
In the case of glucose we must remember that both D and L configuration are dextrorotatory. This is also the same reason why glucose is also known as dextrose. This can be further understood from the Fischer projection of the diagrams below:
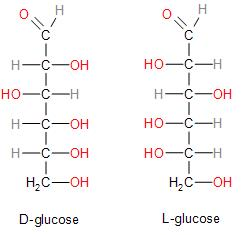
Since we have established the fact that D and L configuration has absolutely no correlation with its optical rotation, we may now conclude that the correct answer is Option (D) Both assertion and reasoning is incorrect.
Additional information:
The prefix used to indicate absolute configuration does not necessarily imply the prefix used to indicate chirality in the same molecule. For example, D-fructose is sometimes called levulose since it is levorotatory.
Note: D-glucose is abundant in nature whereas L-glucose is mostly synthesized in laboratories. Likewise, whenever we digest glucose, it's almost always in the form of D-glucose, because humans don't use L-glucose in their aerobic pathways.
Complete step by step answer:
In a Fischer projection, we see that the L isomers have the hydroxyl group attached to the left side of the penultimate asymmetric carbon and hydrogen on the right, while D isomers have the hydroxyl group on the right side. This assignment of D and L is used to distinguish between two molecules that are enantiomers that should mean they have a relationship on the basis of reflection; with one molecule being a mirror image of the other.
On the other hand, dextrorotation and levorotation simply refers to the rotation of an optically active compound by a plane polarized light. From the point of view of the observer, a dextrorotatory compound rotates the light clockwise towards the right side whereas a levorotatory compound rotates in anticlockwise towards the left side.
In the case of glucose we must remember that both D and L configuration are dextrorotatory. This is also the same reason why glucose is also known as dextrose. This can be further understood from the Fischer projection of the diagrams below:

Since we have established the fact that D and L configuration has absolutely no correlation with its optical rotation, we may now conclude that the correct answer is Option (D) Both assertion and reasoning is incorrect.
Additional information:
The prefix used to indicate absolute configuration does not necessarily imply the prefix used to indicate chirality in the same molecule. For example, D-fructose is sometimes called levulose since it is levorotatory.
Note: D-glucose is abundant in nature whereas L-glucose is mostly synthesized in laboratories. Likewise, whenever we digest glucose, it's almost always in the form of D-glucose, because humans don't use L-glucose in their aerobic pathways.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




