
ASSERTION: ${H_3} B {O_3} $ is monobasic Lewis acid but its salt $N {a_3} B {O_3} $exists.
REASON: ${H_3} B {O_3} $ reacts with $NaOH$ to give $N {a_3} B {O_3} $ in ethyl alcohol.
A.Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation for assertion.
B.Both assertion and reason are correct. But reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
C.Assertion is correct. But the reason is correct.
D.Assertion is incorrect. But the reason is correct.
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: First we need to understand what monobasic Lewis acid is. ${H_3} B {O_3} $ has three $'OH'$ groups so is said to be a tribasic acid, but it also behaves as a monobasic acid. Boric acid accepts a pair of electrons rather than donating one.
Complete step by step answer:
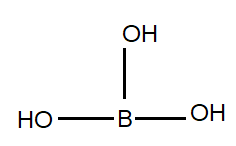
After seeing this structure we can say that boric acid is a tribasic Lewis acid but it’s one of the properties is to act like a monobasic acid to understand this let’s look at the reaction of boric acid.
${H_3} B {O_3} + NaOH \to Nab {(OH) _4} $
\[2{C_2}{H_5}OH + {H_3}B{O_3} \to {({C_2}{H_5})_3}B{O_3}\xrightarrow{{3NaOH}}N{a_3}B{O_3}\].
This compound $NaB{(OH)_4}$ doesn’t react directly with $NaOH$, it first reacts with \[2{C_2}{H_5}OH\] and then it reacts with $NaOH$.
So our answer will be B. Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
Additional information:
The boric acid is a tribasic acid because it has \[3\]$'OH'$ but it also acts as a monobasic acid as well. Because boric acid accepts the proton rather than donating a proton. Boric acid is also known as hydrogen borate, boracic acid and orthoboric acid. And orthoboric acid is a weak Lewis acid. It is used as an antiseptic, insecticide, and flame retardant. Boric acid is colourless crystals, or white powder and it dissolves in water. The mineral of boric acid is known as sassolite. Boric acid is soluble in lower alcohols, moderately soluble in pyridine and very slightly soluble in acetone. Its molecular shape is trigonal planar. The dipole moment of boric acid is zero.
Note:
Monobasic acids are those acids which can only donate $1$ hydrogen atom. If these acids can donate $2{{or}} 3$ they are known as di and tribasic acids. Boric acid when mixed inside water accepts $'OH'$ ions and acts as Lewis acid.
Complete step by step answer:

After seeing this structure we can say that boric acid is a tribasic Lewis acid but it’s one of the properties is to act like a monobasic acid to understand this let’s look at the reaction of boric acid.
${H_3} B {O_3} + NaOH \to Nab {(OH) _4} $
\[2{C_2}{H_5}OH + {H_3}B{O_3} \to {({C_2}{H_5})_3}B{O_3}\xrightarrow{{3NaOH}}N{a_3}B{O_3}\].
This compound $NaB{(OH)_4}$ doesn’t react directly with $NaOH$, it first reacts with \[2{C_2}{H_5}OH\] and then it reacts with $NaOH$.
So our answer will be B. Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
Additional information:
The boric acid is a tribasic acid because it has \[3\]$'OH'$ but it also acts as a monobasic acid as well. Because boric acid accepts the proton rather than donating a proton. Boric acid is also known as hydrogen borate, boracic acid and orthoboric acid. And orthoboric acid is a weak Lewis acid. It is used as an antiseptic, insecticide, and flame retardant. Boric acid is colourless crystals, or white powder and it dissolves in water. The mineral of boric acid is known as sassolite. Boric acid is soluble in lower alcohols, moderately soluble in pyridine and very slightly soluble in acetone. Its molecular shape is trigonal planar. The dipole moment of boric acid is zero.
Note:
Monobasic acids are those acids which can only donate $1$ hydrogen atom. If these acids can donate $2{{or}} 3$ they are known as di and tribasic acids. Boric acid when mixed inside water accepts $'OH'$ ions and acts as Lewis acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




