
Assertion: Pentane and $2 - $ methyl pentane are homologues.
Reason: Pentane is a straight chain alkane, while $2 - $ methyl pentane is a branched chain alkane.
A.Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B.Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C.Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
D.Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer
516k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, we must know the molecular formula of pentane and $2 - $ methyl pentane. By knowing the formula, we will be able to draw their structures. It is necessary to understand the definition of homologues and find out whether the above given compounds are homologues or not.
Complete answer:
Pentane, as the name signifies, “pent” $ + $ "ane” ,is a five carbon alkane with the molecular formula ${C_5}{H_{12}}$ .Given below is the structure of pentane.
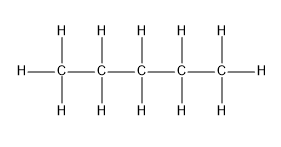
The above picture suggests that pentane is a straight chain alkane.
$2 - $ methyl pentane will have a methyl group attached to the second carbon of pentane and has the molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{14}}$ . The structure will be:
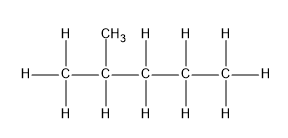
Here, we can notice a branching at the second carbon and therefore it is a branched chain alkane.
Now, we have to find whether both these compounds are homologues or not. A series of compounds with similar chemical properties and functional groups are called homologous series. They share the same general formula and show a gradual variation in their physical properties. The successive members of this series differ by a repeating unit - methylene $(C{H_2})$ group.
While considering the compounds pentane and $2 - $ methyl pentane , we can observe a difference of
$C{H_2}$ group in their molecular formulas and they have the same general formula $({C_n}{H_{2n + 2}})$ . Thus we can conclude that the given compounds are homologues and this is not because the former is a straight chain and the latter is a branched chain alkane.
Therefore, the right option is (B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
Note:
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. The general structural formula of alkanes is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where n represents the number of carbon atoms.
In the alkane family, methane $(C{H_4})$ is the first member of the homologous series followed by ethane $({C_2}{H_6})$ . They differ by a $({C_2}{H_6})$ group.
Complete answer:
Pentane, as the name signifies, “pent” $ + $ "ane” ,is a five carbon alkane with the molecular formula ${C_5}{H_{12}}$ .Given below is the structure of pentane.

The above picture suggests that pentane is a straight chain alkane.
$2 - $ methyl pentane will have a methyl group attached to the second carbon of pentane and has the molecular formula ${C_6}{H_{14}}$ . The structure will be:

Here, we can notice a branching at the second carbon and therefore it is a branched chain alkane.
Now, we have to find whether both these compounds are homologues or not. A series of compounds with similar chemical properties and functional groups are called homologous series. They share the same general formula and show a gradual variation in their physical properties. The successive members of this series differ by a repeating unit - methylene $(C{H_2})$ group.
While considering the compounds pentane and $2 - $ methyl pentane , we can observe a difference of
$C{H_2}$ group in their molecular formulas and they have the same general formula $({C_n}{H_{2n + 2}})$ . Thus we can conclude that the given compounds are homologues and this is not because the former is a straight chain and the latter is a branched chain alkane.
Therefore, the right option is (B) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
Note:
Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. The general structural formula of alkanes is ${C_n}{H_{2n + 2}}$ where n represents the number of carbon atoms.
In the alkane family, methane $(C{H_4})$ is the first member of the homologous series followed by ethane $({C_2}{H_6})$ . They differ by a $({C_2}{H_6})$ group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




