
Assertion: The resistance of a milliammeter is greater than that of ammeter
Reason: Shunt resistance in case of a milliammeter is more than that of ammeter
A. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
B. Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of A
C. (A) is true but (R) is false
D. (A) is false but (R) is true
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint:This problem is based on the variation of shunt resistance of a galvanometer such that a galvanometer must be suitable for milliammeter and ammeter respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:
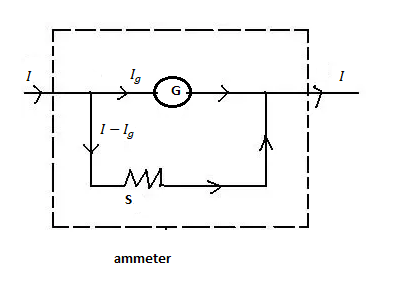
In the figure, $I = $ main current through the ammeter, $G = $galvanometer,${I_g} = $current through the galvanometer, $S = $shunt resistance of the circuit, $I - {I_g} = $the current through the shunt resistance .
Step 2:
In the given circuit diagram the value of the shunt resistance is,
$ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{I_g}G}}{{I - {I_g}}}$.
Now for a given circuit the resistance of galvanometer $G$ is constant and also current through galvanometer ${I_g}$is also constant. Therefore the value of shunt resistance $S$is inversely proportional with the circuit main current that is galvanometer current that is$I$.
i.e.$ \Rightarrow S \propto \dfrac{1}{I}$, where $S = $the shunt resistance and $I = $current through the ammeter.
And the two resistances $G$and $S$are in parallel combination. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the ammeter is,
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$.
Step 3:
Now,
${I_{ammeter}} > {I_{milliammeter}}$
Where, ${I_{ammeter}} = $ current through ammeter and ${I_{milliammeter}} = $current through milliammeter.
$\because $$ \Rightarrow S \propto \dfrac{1}{I}$
$\therefore $${S_{ammeter}} < {S_{milliammeter}}$ ,
Where, ${S_{ammeter}} = $shunt resistance for ammeter and ${S_{milliammeter}} = $shunt resistance for milliammeter.
Therefore the reason is correct.
Step 4:
The equivalent resistance is,
${R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{G}{{\dfrac{G}{S} + 1}}$
Now for a given circuit $G$is constant. Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} \propto S$
$\because $$ \Rightarrow {S_{ammeter}} < {S_{milliammeter}}$
$\therefore $$ \Rightarrow {R_{ammeter}} < {R_{milliammeter}}$,
Where, ${R_{ammeter}} = $resistance of the ammeter and ${R_{milliammeter}} = $ resistance of the milliammeter.
Therefore, the assertion is correct.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
$\therefore $option (A) is the correct option.
Note:Students must remember the circuit diagram for this ammeter circuit. Basically it is the conversion of a galvanometer into an ammeter by using a shunt resistance parallel to the galvanometer.
Also remember the value of shunt resistance and equivalent resistance of the circuit. These are, $ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{I_g}G}}{{I - {I_g}}}$ where, $I = $ main current through the ammeter, $G = $galvanometer,${I_g} = $current through the galvanometer, $S = $shunt resistance of the circuit, $I - {I_g} = $the current through the shunt resistance.
And $ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$
Where, ${R_{equivalent}} = $the equivalent resistance of the ammeter.
Complete step by step solution:
Step 1:

In the figure, $I = $ main current through the ammeter, $G = $galvanometer,${I_g} = $current through the galvanometer, $S = $shunt resistance of the circuit, $I - {I_g} = $the current through the shunt resistance .
Step 2:
In the given circuit diagram the value of the shunt resistance is,
$ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{I_g}G}}{{I - {I_g}}}$.
Now for a given circuit the resistance of galvanometer $G$ is constant and also current through galvanometer ${I_g}$is also constant. Therefore the value of shunt resistance $S$is inversely proportional with the circuit main current that is galvanometer current that is$I$.
i.e.$ \Rightarrow S \propto \dfrac{1}{I}$, where $S = $the shunt resistance and $I = $current through the ammeter.
And the two resistances $G$and $S$are in parallel combination. Therefore, the equivalent resistance of the ammeter is,
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$.
Step 3:
Now,
${I_{ammeter}} > {I_{milliammeter}}$
Where, ${I_{ammeter}} = $ current through ammeter and ${I_{milliammeter}} = $current through milliammeter.
$\because $$ \Rightarrow S \propto \dfrac{1}{I}$
$\therefore $${S_{ammeter}} < {S_{milliammeter}}$ ,
Where, ${S_{ammeter}} = $shunt resistance for ammeter and ${S_{milliammeter}} = $shunt resistance for milliammeter.
Therefore the reason is correct.
Step 4:
The equivalent resistance is,
${R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{G}{{\dfrac{G}{S} + 1}}$
Now for a given circuit $G$is constant. Therefore,
$ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} \propto S$
$\because $$ \Rightarrow {S_{ammeter}} < {S_{milliammeter}}$
$\therefore $$ \Rightarrow {R_{ammeter}} < {R_{milliammeter}}$,
Where, ${R_{ammeter}} = $resistance of the ammeter and ${R_{milliammeter}} = $ resistance of the milliammeter.
Therefore, the assertion is correct.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of A.
$\therefore $option (A) is the correct option.
Note:Students must remember the circuit diagram for this ammeter circuit. Basically it is the conversion of a galvanometer into an ammeter by using a shunt resistance parallel to the galvanometer.
Also remember the value of shunt resistance and equivalent resistance of the circuit. These are, $ \Rightarrow S = \dfrac{{{I_g}G}}{{I - {I_g}}}$ where, $I = $ main current through the ammeter, $G = $galvanometer,${I_g} = $current through the galvanometer, $S = $shunt resistance of the circuit, $I - {I_g} = $the current through the shunt resistance.
And $ \Rightarrow {R_{equivalent}} = \dfrac{{GS}}{{G + S}}$
Where, ${R_{equivalent}} = $the equivalent resistance of the ammeter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




