
Assertion: Wobble hypothesis explains the phenomena of multiple codons coding for the code of a single amino acid.
Reason: One tRNA molecule can recognise and bind to more than one codon, due to less-precise base pairs.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion
C. Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect
D. Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect
Answer
505.8k+ views
Hint: The Wobble Hypothesis explains why multiple codons can code for a single amino acid. A wobble base pair is a pairing between two nucleotides in RNA molecules that does not follow Watson-Crick base pair rules.
Complete Answer:
The Wobble Hypothesis, by Francis Crick, states that the 3rd base in an mRNA codon can undergo non-Watson-Crick base pairing with the 1st base of a tRNA anticodon. The four main wobble base pairs are guanine-uracil (G-U), hypoxanthine-uracil (I-U), hypoxanthine-adenine (I-A), and hypoxanthine-cytosine (I-C). In order to maintain the consistency of nucleic acid nomenclature, "I" is used for hypoxanthine because hypoxanthine is the nucleobase of inosine.
In the genetic code, there are 64 possible codons (3 nucleotide sequences). For translation, each of these codons require a tRNA molecule with an anticodon with which it can complement in a stable condition. If each tRNA molecule is paired with its complementary mRNA codon following the Watson-Crick base pairing, then 64 types of tRNA molecule will be required. In a standard genetic code, 3 of the 64 mRNA codons (UAA, UAG and UGA) are stop codons, i.e., they terminate the translation process by binding itself to release factors rather than tRNA molecules. Therefore, a pairing would require 61 species of tRNA. Most organisms have fewer than 45 types of tRNA, so a few tRNA types pair with multiple, synonymous codons all of which encode the same amino acid. In 1966, Francis Crick proposed the Wobble Hypothesis to account for this characteristic. He postulated that the 5' base on the anticodon which binds to the 3' base on the mRNA, is not as spatially confined as the other two bases. Thereby, they could have non-standard base pairing. Crick creatively named it for the small amount of "play" or wobble that happens at this third codon position. Movement (or "wobble") of the base in the 5' anticodon position happens for small conformational adjustments that are necessary for the overall pairing geometry of anticodons of tRNA.
Hence, option (A) both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion is the correct option since the Wobble hypothesis was established to explain the multiple binding characteristic of the tRNA molecules.
Note:
Wobble base pairs have been shown to facilitate many biological functions. It was most clearly demonstrated in the bacterium Escherichia coli. In fact, in a study of E. coli's tRNA for alanine, it was seen that there is a wobble base pair that determines whether the tRNA will be aminoacylated.
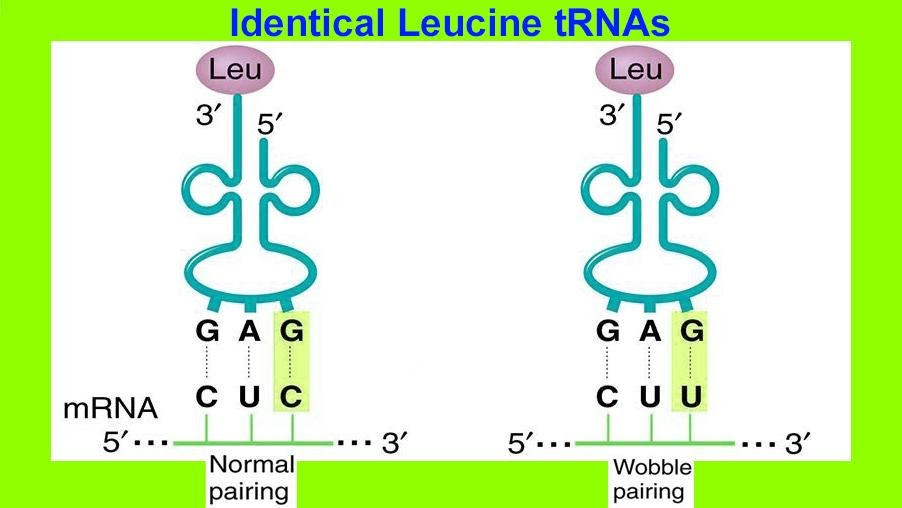
Figure: tRNA
Complete Answer:
The Wobble Hypothesis, by Francis Crick, states that the 3rd base in an mRNA codon can undergo non-Watson-Crick base pairing with the 1st base of a tRNA anticodon. The four main wobble base pairs are guanine-uracil (G-U), hypoxanthine-uracil (I-U), hypoxanthine-adenine (I-A), and hypoxanthine-cytosine (I-C). In order to maintain the consistency of nucleic acid nomenclature, "I" is used for hypoxanthine because hypoxanthine is the nucleobase of inosine.
In the genetic code, there are 64 possible codons (3 nucleotide sequences). For translation, each of these codons require a tRNA molecule with an anticodon with which it can complement in a stable condition. If each tRNA molecule is paired with its complementary mRNA codon following the Watson-Crick base pairing, then 64 types of tRNA molecule will be required. In a standard genetic code, 3 of the 64 mRNA codons (UAA, UAG and UGA) are stop codons, i.e., they terminate the translation process by binding itself to release factors rather than tRNA molecules. Therefore, a pairing would require 61 species of tRNA. Most organisms have fewer than 45 types of tRNA, so a few tRNA types pair with multiple, synonymous codons all of which encode the same amino acid. In 1966, Francis Crick proposed the Wobble Hypothesis to account for this characteristic. He postulated that the 5' base on the anticodon which binds to the 3' base on the mRNA, is not as spatially confined as the other two bases. Thereby, they could have non-standard base pairing. Crick creatively named it for the small amount of "play" or wobble that happens at this third codon position. Movement (or "wobble") of the base in the 5' anticodon position happens for small conformational adjustments that are necessary for the overall pairing geometry of anticodons of tRNA.
Hence, option (A) both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion is the correct option since the Wobble hypothesis was established to explain the multiple binding characteristic of the tRNA molecules.
Note:
Wobble base pairs have been shown to facilitate many biological functions. It was most clearly demonstrated in the bacterium Escherichia coli. In fact, in a study of E. coli's tRNA for alanine, it was seen that there is a wobble base pair that determines whether the tRNA will be aminoacylated.

Figure: tRNA
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




