
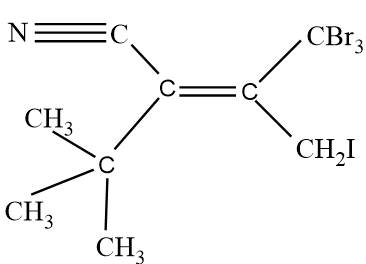
Assign E/Z configuration:

Answer
521.3k+ views
Hint: Groups around the double bond are assigned priority according to the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog-priority rules. E/Z is a type of geometrical isomer. Configuration is seen by the different spatial arrangement of atoms around the double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are those which have the same molecular formula and have different spatial arrangements. Isomers are of two types, geometrical isomers and Optical isomers. Geometrical isomers are of three types- cis-trans, E-Z type, syn-anti isomers.
E/Z terminology is used when no same groups are present on the sides of a double bond. Then, on both the sides, groups are assigned priority according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog-priority rules. So when groups of the same priority are on the same side, it is called Z type isomers ,and when groups of same priority are on different sides it is called E type isomers.
Priority is assigned according to their atomic number. The atom with higher atomic number is assigned high priority and atom with lower priority number.
So in the given molecule, On both sides of the double bond, we will analyse the atoms, and we will assign priority accordingly. On the left hand side, we have one CN molecule and $C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}$ molecule. So going according to the CIP rule, We see that atomic number of Nitrogen Is higher than carbon, so group with CN molecule will get higher priority that is 1, and the other group with $C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}$ will have lower priority that is 2. Same procedure will be done for the right hand side of the double bond. Since one group has Bromine and the other group have iodine alongside carbon. An atomic number of bromine is less than iodine, therefore, a group with Iodine will have higher priority that is 1 as compared to a group having bromine atoms. Groups with bromine atoms will be given 2 priority.
Now after allotting the priority, we see that groups with the same priority are on different sides, therefore it will be an Z type isomer.
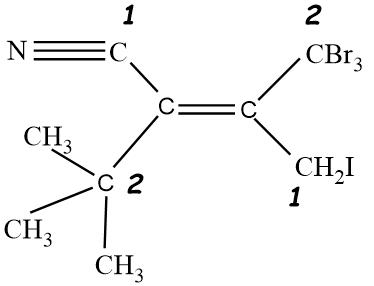
So, the given compound is having Z configuration.
Note: Cis-trans terminology is used when there are two same types of groups attached on the sides of the double bond. When same groups are attached on adjacent sides, it is called cis isomer, and when same group is attached on different sides then it called trans isomer.
Complete step by step answer:
Isomers are those which have the same molecular formula and have different spatial arrangements. Isomers are of two types, geometrical isomers and Optical isomers. Geometrical isomers are of three types- cis-trans, E-Z type, syn-anti isomers.
E/Z terminology is used when no same groups are present on the sides of a double bond. Then, on both the sides, groups are assigned priority according to Cahn-Ingold-Prelog-priority rules. So when groups of the same priority are on the same side, it is called Z type isomers ,and when groups of same priority are on different sides it is called E type isomers.
Priority is assigned according to their atomic number. The atom with higher atomic number is assigned high priority and atom with lower priority number.
So in the given molecule, On both sides of the double bond, we will analyse the atoms, and we will assign priority accordingly. On the left hand side, we have one CN molecule and $C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}$ molecule. So going according to the CIP rule, We see that atomic number of Nitrogen Is higher than carbon, so group with CN molecule will get higher priority that is 1, and the other group with $C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}$ will have lower priority that is 2. Same procedure will be done for the right hand side of the double bond. Since one group has Bromine and the other group have iodine alongside carbon. An atomic number of bromine is less than iodine, therefore, a group with Iodine will have higher priority that is 1 as compared to a group having bromine atoms. Groups with bromine atoms will be given 2 priority.
Now after allotting the priority, we see that groups with the same priority are on different sides, therefore it will be an Z type isomer.

So, the given compound is having Z configuration.
Note: Cis-trans terminology is used when there are two same types of groups attached on the sides of the double bond. When same groups are attached on adjacent sides, it is called cis isomer, and when same group is attached on different sides then it called trans isomer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




