
What is the atomic number of Fe in ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$?
A. 35
B. 36
C. 37
D. Cannot be calculated
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: In the above question, it is asked about EAN value of Fe in ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$. For finding the EAN value, we have to find the atomic number and oxidation number of Fe and number of electrons donated by the ligands.
Formula Used-
EAN = \[Z - X + Y\]
where Z= atomic number of the central atom
X= oxidation number of central atom
Y= No. of electrons donated by ligand
Complete step-by-step answer:Effective Atomic Number (EAN) is the number that represents the total number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of a metal atom in a metal complex.
According to EAN rule, a metal atom tends to surround itself with sufficient ligands such that the resulting effective atomic number is equal to the atomic number of the noble gas element which is found in the same period in which the metal is situated.
Let us now find out EAN value of ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$.
Z= atomic number of Fe = $26$
Since, the charge of CO is 0 as it is a neutral ligand, hence oxidation state of Fe can be found out by:
9${{ \times }}$ Charge of CO + 2 ${{ \times }}$ Charge of Fe = Charge on the complex
$ \Rightarrow 9 \times 0 + 2 \times x = 0$
So, X=0
For finding Y, we have to look at the structure of ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$
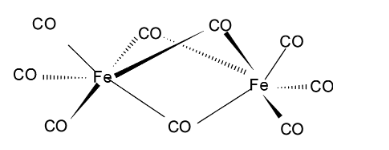
Since, the 3 terminal bonds for each Fe share 2 electrons each while the middle common bonds share 1 electron.
So, Y=$3 \times 2 + 3 = 9$.
EAN =\[Z - X + Y\] = $26 - 0 + 9 = 35$
Therefore, the correct option is option A.
Note:EAN rule is valid for metal complexes with carbon monoxide, metal carbonyl as well as many organometallic compounds.
By using this rule, it is possible to predict the number of ligands in the compounds.
Formula Used-
EAN = \[Z - X + Y\]
where Z= atomic number of the central atom
X= oxidation number of central atom
Y= No. of electrons donated by ligand
Complete step-by-step answer:Effective Atomic Number (EAN) is the number that represents the total number of electrons surrounding the nucleus of a metal atom in a metal complex.
According to EAN rule, a metal atom tends to surround itself with sufficient ligands such that the resulting effective atomic number is equal to the atomic number of the noble gas element which is found in the same period in which the metal is situated.
Let us now find out EAN value of ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$.
Z= atomic number of Fe = $26$
Since, the charge of CO is 0 as it is a neutral ligand, hence oxidation state of Fe can be found out by:
9${{ \times }}$ Charge of CO + 2 ${{ \times }}$ Charge of Fe = Charge on the complex
$ \Rightarrow 9 \times 0 + 2 \times x = 0$
So, X=0
For finding Y, we have to look at the structure of ${\text{F}}{{\text{e}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{(CO)}}_{\text{9}}}$

Since, the 3 terminal bonds for each Fe share 2 electrons each while the middle common bonds share 1 electron.
So, Y=$3 \times 2 + 3 = 9$.
EAN =\[Z - X + Y\] = $26 - 0 + 9 = 35$
Therefore, the correct option is option A.
Note:EAN rule is valid for metal complexes with carbon monoxide, metal carbonyl as well as many organometallic compounds.
By using this rule, it is possible to predict the number of ligands in the compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




