
Bacteria present in root nodules of the leguminous plants are
A) Rhizobium
B) Lactobacillus
C) Cyanobacteria
D) Azotobacter
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: A bacteria which helps in fixing the nitrogen of the atmosphere in the roots of the leguminous plants to convert nitrogen into a more accessible form.
Complete Answer:
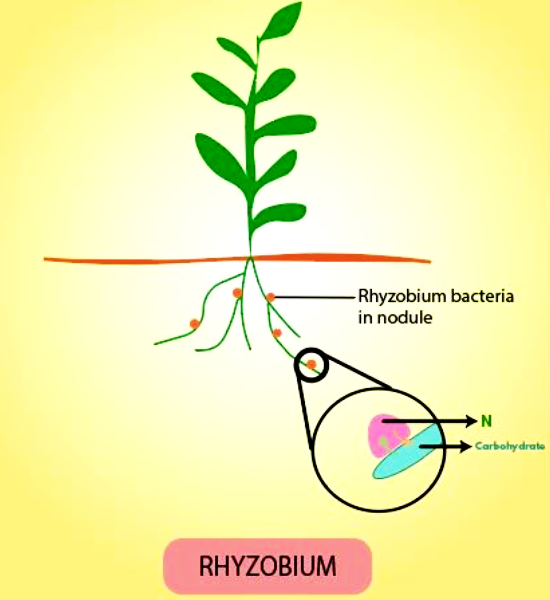
Rhizobium is a gram-negative, motile soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. They form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants. They live in the root nodules of the plants and convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia with the help of an enzyme called nitrogenase. This form of nitrogen can easily be absorbed by the plants.
Additional information:
-The rhizobium bacteria form a symbiotic relationship with leguminous plants and both benefit each other.
-The bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and provide organic nitrogenous substances like glutamine or ureides to the plant.
-In return, the plant will provide organic compounds to the bacteria which was made during the process of photosynthesis.
-Rhizobium bacteria form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with the roots of legumes and Parasponia plants.
-The ammonia formed in this process acts as a natural fertilizer for the plants.
-Root nodules eat the swelling on the roots of certain plants that contain bacteria to fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and convert nitrates into amino acids.
So, the correct answer is ‘Rhizobium’.
Note: Martinus Beijerinck in 1888 was the first to isolate a microorganism from the root nodules of the leguminous plants. Firstly, he named it Bacillus radicicola, which is now under the genus Rhizobium. It is now used in many research works that involve genetic mapping of rhizobium with their symbiotic plants to increase plant productivity without using any fertilizer.
Complete Answer:
Rhizobium is a gram-negative, motile soil bacteria that fix nitrogen. They form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of the leguminous plants. They live in the root nodules of the plants and convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia with the help of an enzyme called nitrogenase. This form of nitrogen can easily be absorbed by the plants.
Additional information:
-The rhizobium bacteria form a symbiotic relationship with leguminous plants and both benefit each other.
-The bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and provide organic nitrogenous substances like glutamine or ureides to the plant.
-In return, the plant will provide organic compounds to the bacteria which was made during the process of photosynthesis.
-Rhizobium bacteria form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with the roots of legumes and Parasponia plants.
-The ammonia formed in this process acts as a natural fertilizer for the plants.
-Root nodules eat the swelling on the roots of certain plants that contain bacteria to fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia and convert nitrates into amino acids.

So, the correct answer is ‘Rhizobium’.
Note: Martinus Beijerinck in 1888 was the first to isolate a microorganism from the root nodules of the leguminous plants. Firstly, he named it Bacillus radicicola, which is now under the genus Rhizobium. It is now used in many research works that involve genetic mapping of rhizobium with their symbiotic plants to increase plant productivity without using any fertilizer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




