
What is the basicity of ${H_3}P{O_2}$ acid and why?
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint:The basicity of an acid is defined by the hydrogen that can be replaced by other residues and it can be determined according to the structure of the acid. The basicity depends on the number of hydrogens associated in this manner and hence they can be replaced proving the level of basic character.
Complete answer:
The basicity of any specific acids depends on the number of hydrogens that can be replaced in the structure of the acid. The structure of the specific acid ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is given below.
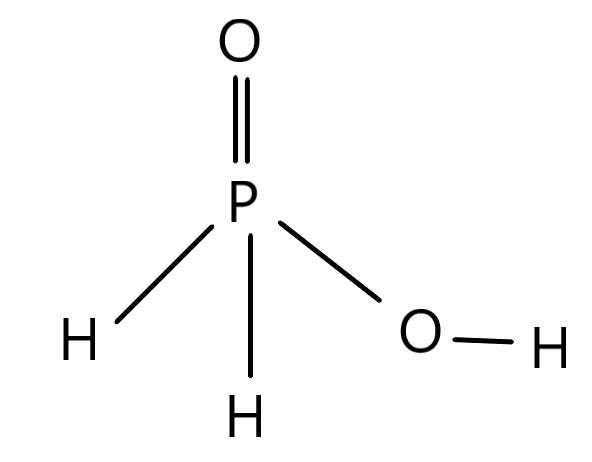
There is the $P$ as the central atom which is Phosphorus which is associated with an oxygen residue $\left( O \right)$ while there are other associated covalent bonds. There are two hydrogen residues which are associated with the central atom while there is one $\left( {OH} \right)$ association with the $P$ residue. This means there is only one $OH$ residue which is present in the whole structure. The replaceable hydrogens are those hydrogen residues which form a bond with the oxygen in this case. The replacement of hydrogen is easier in this case because there is a chance of hydrogen being replaced at this position owing to the electronegative character of the oxygen residue. Since there is only one $\left( {OH} \right)$ association therefore the basicity for the acid ${H_3}P{O_2}$ will be $1$. This way the basicity of any acid can be calculated.
Note:
The chances of finding the basicity depends on the fact if the structure of the given compound can be determined. Once the structure is defined the specific type of hydrogen can be seen from the structure.
Complete answer:
The basicity of any specific acids depends on the number of hydrogens that can be replaced in the structure of the acid. The structure of the specific acid ${H_3}P{O_2}$ is given below.

There is the $P$ as the central atom which is Phosphorus which is associated with an oxygen residue $\left( O \right)$ while there are other associated covalent bonds. There are two hydrogen residues which are associated with the central atom while there is one $\left( {OH} \right)$ association with the $P$ residue. This means there is only one $OH$ residue which is present in the whole structure. The replaceable hydrogens are those hydrogen residues which form a bond with the oxygen in this case. The replacement of hydrogen is easier in this case because there is a chance of hydrogen being replaced at this position owing to the electronegative character of the oxygen residue. Since there is only one $\left( {OH} \right)$ association therefore the basicity for the acid ${H_3}P{O_2}$ will be $1$. This way the basicity of any acid can be calculated.
Note:
The chances of finding the basicity depends on the fact if the structure of the given compound can be determined. Once the structure is defined the specific type of hydrogen can be seen from the structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




