
What is the basis of sex determination in human beings? Explain.
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint:Most organisms give birth by the method of sexual reproduction between male and female. The sex determination in an organism defines the sexual characteristics of the organism which identifies them as males or females.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the sex determination in human beings.
Humans contain 23 pairs or 46 numbers of chromosomes. Out of which 22 pairs are called the autosomes and the $23^{rd}$ pair is the sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are X and Y. A female has XX chromosomes in their cell. Male contains XY. The gametes are formed by the process of meiosis which is a reduction division. To keep the number of chromosomes constant gametes are formed by the process of meiosis and not mitosis. The male gamete is fused with the female gamete after sexual intercourse and sexual reproduction takes place.
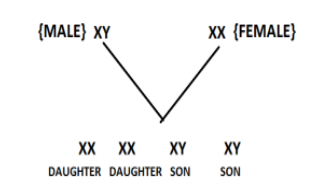
The sex of the child is therefore dependent that which chromosome the male or father will transfer and female will always transfer the X chromosome. If the male transfers an X chromosome, the offspring born will be XX (female) But if the male transfers the Y chromosome then a male will be born (XY).
Note: In human beings the females are homozygous containing similar alleles of X whereas males are heterozygous which contains a copy of X and Y. In various organisms sex is determined by the environmental factors. In some species there is only one sex where the female reproduces without fertilisation.
Complete answer:
To answer this question, we must know about the sex determination in human beings.
Humans contain 23 pairs or 46 numbers of chromosomes. Out of which 22 pairs are called the autosomes and the $23^{rd}$ pair is the sex chromosomes. The sex chromosomes are X and Y. A female has XX chromosomes in their cell. Male contains XY. The gametes are formed by the process of meiosis which is a reduction division. To keep the number of chromosomes constant gametes are formed by the process of meiosis and not mitosis. The male gamete is fused with the female gamete after sexual intercourse and sexual reproduction takes place.

The sex of the child is therefore dependent that which chromosome the male or father will transfer and female will always transfer the X chromosome. If the male transfers an X chromosome, the offspring born will be XX (female) But if the male transfers the Y chromosome then a male will be born (XY).
Note: In human beings the females are homozygous containing similar alleles of X whereas males are heterozygous which contains a copy of X and Y. In various organisms sex is determined by the environmental factors. In some species there is only one sex where the female reproduces without fertilisation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




