
Bb Roy great britain very good wife. What does this sentence say?
Answer
460.5k+ views
Hint: If you know how to read coloured bands on a resistor, you can learn everything you need to know about its value and tolerance. The order in which the colours are displayed is crucial, and each resistor value has its own distinct combination.
Complete answer:
The BBROYGBVGW alphabets are represented by BB ROY of Great Britain's very good wife. This is an electronic colour code that memorises component colours such as resistors, condensers, inductors, and diodes to display values. The colour is identified using this code sentence. BBROYGBVGW stands for a variety of colours, including:-
B – Black
B – Brown
R – Red
O – Orange
Y – Yellow
G – Green
B – Blue
V – Violet
G – Grey
W- White
In general, code refers to the representation of information in another form for the purpose of secrecy using symbols, signals, and letters. Signals or symbols are used as codes in this case. Similarly, different colours are used as codes in resistors to specify the resistance (information) of the resistor. The different colours on the resistor serve as codes in this case.
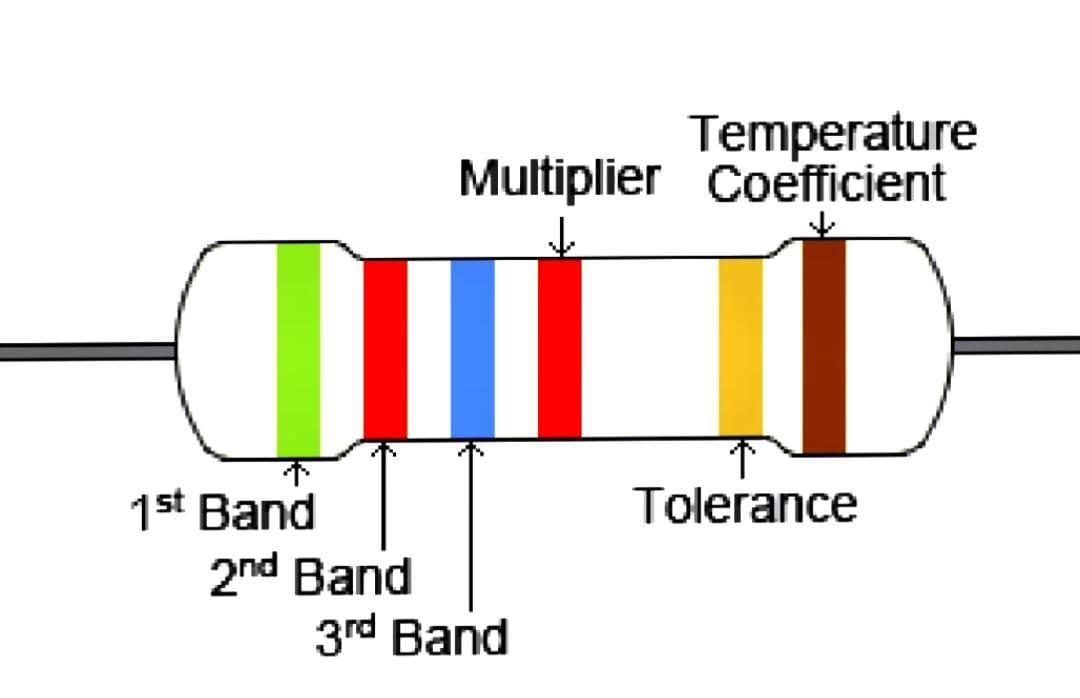
The values of resistors are denoted by this small coloured stripes. The first two stripes are numerical values, while the third is a multiplier. The fourth stripe indicates the tolerance of the resistor, i.e., how close to the indicated value you can expect the resistance to be in reality.
Note:
Because the colour coding technique only shows a fixed resistance value, it should be noted that color-coding is only done in fixed resistors and not in variable resistors. The resistance of variable resistors varies. As a result, the colour coding technique cannot be used in variable resistors.
Complete answer:
The BBROYGBVGW alphabets are represented by BB ROY of Great Britain's very good wife. This is an electronic colour code that memorises component colours such as resistors, condensers, inductors, and diodes to display values. The colour is identified using this code sentence. BBROYGBVGW stands for a variety of colours, including:-
B – Black
B – Brown
R – Red
O – Orange
Y – Yellow
G – Green
B – Blue
V – Violet
G – Grey
W- White
In general, code refers to the representation of information in another form for the purpose of secrecy using symbols, signals, and letters. Signals or symbols are used as codes in this case. Similarly, different colours are used as codes in resistors to specify the resistance (information) of the resistor. The different colours on the resistor serve as codes in this case.
The values of resistors are denoted by this small coloured stripes. The first two stripes are numerical values, while the third is a multiplier. The fourth stripe indicates the tolerance of the resistor, i.e., how close to the indicated value you can expect the resistance to be in reality.

Note:
Because the colour coding technique only shows a fixed resistance value, it should be noted that color-coding is only done in fixed resistors and not in variable resistors. The resistance of variable resistors varies. As a result, the colour coding technique cannot be used in variable resistors.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




