
Benzene diazonium chloride on hydrolysis gives:
(A)Benzene
(B)Benzyl Alcohol
(C)Phenol
(D)Chlorobenzene
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group, $R-{{N}_{2}}^{+}{{X}^{-}}$, where R can be any organic group. Many diazonium salts are susceptible to displacement reactions by various substrates, generating nitrogen as a by-product.
Complete step by step solution:
Benzene diazonium chloride is an organic compound with the formula $({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}{{N}_{2}})Cl$. The structure of Benzene diazonium chloride is as follows:
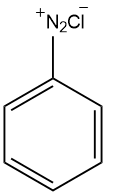
It is a salt of a diazonium cation and chloride. It exists as a colourless solid that is soluble in polar solvents including water. Benzene diazonium chloride can be formed by first mixing benzene with nitric acid, which forms nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene can then be transformed into aniline and aniline can be mixed with nitrous acid in the presence of hydrochloric acid to form the benzene diazonium chloride molecule. During the preparation of Benzene diazonium chloride, lower temperatures are favoured it because the formed Benzene diazonium chloride will become unstable if the temperature becomes more than ${{5}^{\circ }}C$
-On hydrolysis of Benzene diazonium chloride, Nitrogen molecules escape as nitrogen gas. The OH group of water attacks the vacant site left after removal of nitrogen gas. This results in the formation of phenol. Also, Small amount of NaCl is also generated.
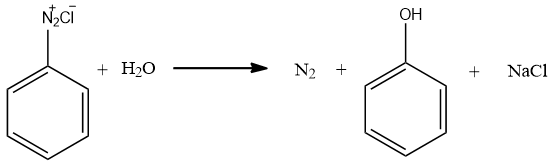
Therefore, the correct answer is (C) option.
Note: Another common pathway is to undergo a coupling reaction to form a diazo compound. Diazonium salts are important synthetic intermediates that can undergo coupling reactions to form azo dyes and electrophilic substitution reactions to introduce functional groups.
Complete step by step solution:
Benzene diazonium chloride is an organic compound with the formula $({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}{{N}_{2}})Cl$. The structure of Benzene diazonium chloride is as follows:

It is a salt of a diazonium cation and chloride. It exists as a colourless solid that is soluble in polar solvents including water. Benzene diazonium chloride can be formed by first mixing benzene with nitric acid, which forms nitrobenzene. Nitrobenzene can then be transformed into aniline and aniline can be mixed with nitrous acid in the presence of hydrochloric acid to form the benzene diazonium chloride molecule. During the preparation of Benzene diazonium chloride, lower temperatures are favoured it because the formed Benzene diazonium chloride will become unstable if the temperature becomes more than ${{5}^{\circ }}C$
-On hydrolysis of Benzene diazonium chloride, Nitrogen molecules escape as nitrogen gas. The OH group of water attacks the vacant site left after removal of nitrogen gas. This results in the formation of phenol. Also, Small amount of NaCl is also generated.

Therefore, the correct answer is (C) option.
Note: Another common pathway is to undergo a coupling reaction to form a diazo compound. Diazonium salts are important synthetic intermediates that can undergo coupling reactions to form azo dyes and electrophilic substitution reactions to introduce functional groups.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




