
Benzene is a resonance hybrid mainly of two Kekule's structures. Hence:
A. Half of the molecules correspond to one structure, and half of the second structure
B. At low temperatures benzene can be separated into two structures
C. Two structures make equal contribution to resonance hybrid
D. An individual benzene molecule changes back and forth between two structures.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint:
-Resonance is a representation of movement of pi electron clouds in a molecule having alternate double bonds.
-All the resonating structures produced by a molecule have equal contribution to the resonance hybrid.
Complete answer:
We know that resonance is a theoretical way used for describing the bonding between certain atoms in a molecule or ions with the help of combination of a number of contributing structures or forms which are generally known as resonating structures, or canonical structures or kekule’s structure.
We know that when a structure undergoes the process of resonance the electron clouds in the double bond gets delocalised throughout the bonds. Given below are the resonating structures of benzene.
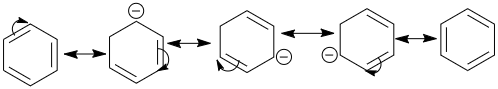
Now if we consider the structures we can see that the electron cloud jumps or gets delocalised in all the carbons one by one giving rise to corresponding resonating structures. All these structures exist theoretically in nature and the kekule’s structure is the final structure which we can observe. It represents the resonance hybrids, which is the sum of all these structures as all of these structures contribute to the final structure of the benzene. All the bonds involved in resonance have equal lengths. The kekule’s structure is given below, in case of benzene,
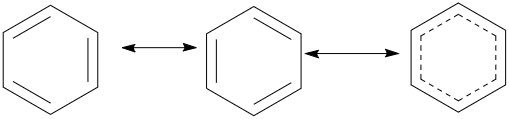
The third structure is the final resonance hybrid which shows that all the bonds are equal in length.
Now if we consider the options given in the question,
option A says half of the molecules correspond to one structure, and half of the second structure, which is obviously not true as we know all of the structures are resonating structures of one another. So option A is incorrect.
Now if we consider option B, it says benzene at low temperature separate into two structures, but we already know that the resonating structures are hypothetical and they doesn’t exist individually, meaning the electron clouds are delocalised on all the carbons, unlike the kekule structures which represents the fixed positions of double bond, hence this option would be incorrect.
Now consider the option C, which says two structures make equal contribution to resonance hybrids, which we already discussed earlier, so this is the most appropriate answer.
And finally, option D says the benzene acquires kekule structures back and forth, again, we know that there is no fixed calculated structure and we cannot say that the benzene changes its electron clouds back and forth, as there is no fixed rule as to which structure it will acquire and when, the kekule structures just gives us an idea that the electrons clouds are delocalised, the electrons could move anywhere in the pi electron clouds, hence option D is inappropriate.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In benzene, both of the resonating kekule’s structures contribute to the resonance hybrid and all the carbon-carbon bonds in a benzene ring have equal lengths.
Resonance is a theoretical effect to get an idea about the movement of electron clouds in the double bonds, and consequently a prediction of the preferable positions of nucleophiles or electrophiles which will attack the original structure.
-Resonance is a representation of movement of pi electron clouds in a molecule having alternate double bonds.
-All the resonating structures produced by a molecule have equal contribution to the resonance hybrid.
Complete answer:
We know that resonance is a theoretical way used for describing the bonding between certain atoms in a molecule or ions with the help of combination of a number of contributing structures or forms which are generally known as resonating structures, or canonical structures or kekule’s structure.
We know that when a structure undergoes the process of resonance the electron clouds in the double bond gets delocalised throughout the bonds. Given below are the resonating structures of benzene.

Now if we consider the structures we can see that the electron cloud jumps or gets delocalised in all the carbons one by one giving rise to corresponding resonating structures. All these structures exist theoretically in nature and the kekule’s structure is the final structure which we can observe. It represents the resonance hybrids, which is the sum of all these structures as all of these structures contribute to the final structure of the benzene. All the bonds involved in resonance have equal lengths. The kekule’s structure is given below, in case of benzene,

The third structure is the final resonance hybrid which shows that all the bonds are equal in length.
Now if we consider the options given in the question,
option A says half of the molecules correspond to one structure, and half of the second structure, which is obviously not true as we know all of the structures are resonating structures of one another. So option A is incorrect.
Now if we consider option B, it says benzene at low temperature separate into two structures, but we already know that the resonating structures are hypothetical and they doesn’t exist individually, meaning the electron clouds are delocalised on all the carbons, unlike the kekule structures which represents the fixed positions of double bond, hence this option would be incorrect.
Now consider the option C, which says two structures make equal contribution to resonance hybrids, which we already discussed earlier, so this is the most appropriate answer.
And finally, option D says the benzene acquires kekule structures back and forth, again, we know that there is no fixed calculated structure and we cannot say that the benzene changes its electron clouds back and forth, as there is no fixed rule as to which structure it will acquire and when, the kekule structures just gives us an idea that the electrons clouds are delocalised, the electrons could move anywhere in the pi electron clouds, hence option D is inappropriate.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In benzene, both of the resonating kekule’s structures contribute to the resonance hybrid and all the carbon-carbon bonds in a benzene ring have equal lengths.
Resonance is a theoretical effect to get an idea about the movement of electron clouds in the double bonds, and consequently a prediction of the preferable positions of nucleophiles or electrophiles which will attack the original structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




