
How benzene is converted into benzaldehyde by Gatterman-Koch reaction? Write equations.
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint:Gatterman-Koch reaction is a reaction by which we can insert formyl group into the aromatic nucleus. Mostly it is used for benzene only but it can also be used in any aromatic compound. A detailed discussion is below. The whole mechanism we should understand in order to convert benzene to benzaldehyde.
Complete answer:
Gatterman-Koch reaction:
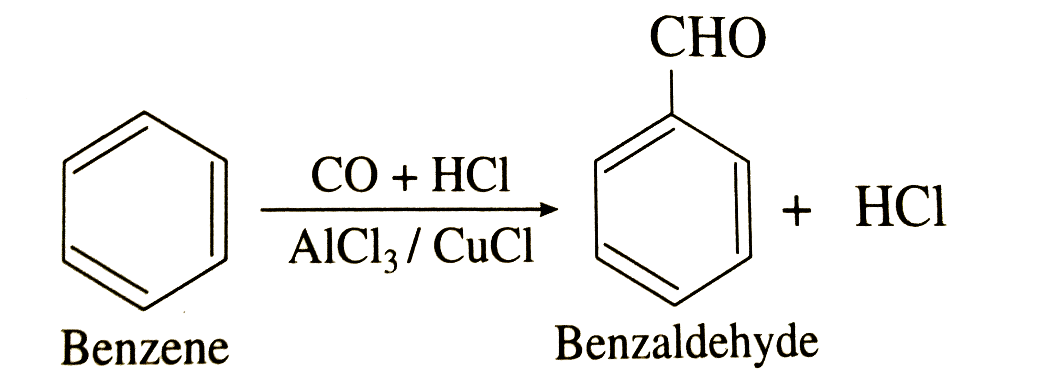
Step 1: The first step of the reaction is the generation of the reactive species which can later be utilized to respond on the aromatic ring. Since carbon monoxide goes about as a Lewis base, it can acknowledge a proton from the hydrochloric acid. This outcome is a decidedly charged particle that has diverse resonance structures. One such resonance structure shows a positive charge on the carbon, clarifying the reactivity of the mixture. This species can go about as an electrophile while responding with the aromatic ring. In any case, it is bound to be the objective of a nucleophilic attack from the chloride ion in the hydrochloric acid.
Step 2: When we add a Lewis acid (aluminium chloride), a chloride ion is removed easily from the species. The species now reverts to the reactive form.
Step 3: After that an electrophilic aromatic substitution occurs at the benzene ring. The benzene ring acts as a nucleophile and donates an electron pair to the formal cation. Then the benzene loses its aromatic property but it is quickly dissolved by the proton expulsion.
Thus, by this method the formyl group can easily attach to the benzene ring via the Gatterman – Koch reaction. In the example shown in the above mechanism, benzaldehyde (\[{C_6}{H_5}CHO\]) is formed from the treatment of benzene with carbon monoxide and hydrochloric acid in the presence of aluminium chloride and copper chloride (Catalyst).
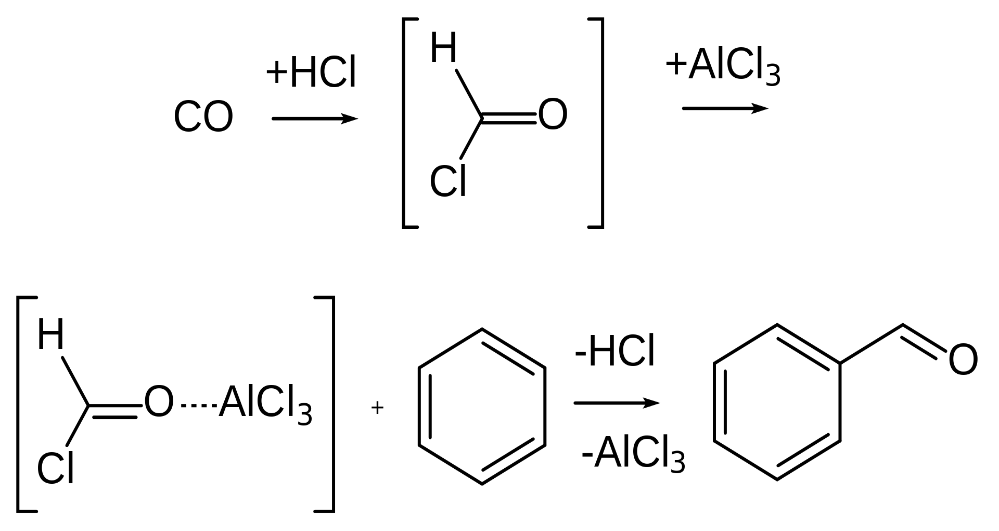
Note: This reaction Mechanism begins with the formation of the reactive species with the help of the acid. The overall aim of the reaction is to attach a formyl group (\[ - CHO\]group) to an aromatic system. And also we should keep this in mind that this reaction is not applicable for phenol and phenol ether substrates.
Complete answer:
Gatterman-Koch reaction:

Step 1: The first step of the reaction is the generation of the reactive species which can later be utilized to respond on the aromatic ring. Since carbon monoxide goes about as a Lewis base, it can acknowledge a proton from the hydrochloric acid. This outcome is a decidedly charged particle that has diverse resonance structures. One such resonance structure shows a positive charge on the carbon, clarifying the reactivity of the mixture. This species can go about as an electrophile while responding with the aromatic ring. In any case, it is bound to be the objective of a nucleophilic attack from the chloride ion in the hydrochloric acid.
Step 2: When we add a Lewis acid (aluminium chloride), a chloride ion is removed easily from the species. The species now reverts to the reactive form.
Step 3: After that an electrophilic aromatic substitution occurs at the benzene ring. The benzene ring acts as a nucleophile and donates an electron pair to the formal cation. Then the benzene loses its aromatic property but it is quickly dissolved by the proton expulsion.
Thus, by this method the formyl group can easily attach to the benzene ring via the Gatterman – Koch reaction. In the example shown in the above mechanism, benzaldehyde (\[{C_6}{H_5}CHO\]) is formed from the treatment of benzene with carbon monoxide and hydrochloric acid in the presence of aluminium chloride and copper chloride (Catalyst).

Note: This reaction Mechanism begins with the formation of the reactive species with the help of the acid. The overall aim of the reaction is to attach a formyl group (\[ - CHO\]group) to an aromatic system. And also we should keep this in mind that this reaction is not applicable for phenol and phenol ether substrates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




