
Benzene on ozonolysis followed by reaction with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$ gives:
(A) 3 moles of glycerol
(B) 3 moles of glyoxal
(C) 3 moles of glyoxalic acid
(D) 3 moles of acetylene
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: Ozonolysis gives a product in which the double bonds are replaced with an ozone molecule. Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$ is a reducing agent. It causes the molecule to break off at the places where there is a carbon-oxygen-carbon bond. The end product is a crystalline solid, which is white at low temperature and yellow near the melting point.
Complete step by step solution:
i) Ozonolysis is an organic reaction in which the oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated bond in a compound occurs when reacted with ozone. The end product will be an organic compound in which multiple carbon – carbon bonds have been replaced with bonds to oxygen.
ii) Here we have to find the end product for ozonolysis of benzene, followed by reaction with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$.
iii) Let us first see what the product will be after ozonolysis of benzene. During ozonolysis of benzene, what happens is an ozone is added to each pi bond of the benzene. Hence the product will be such that in the place of a double bond, there will be 2 O atoms attached as a chain outside the ring in between the 2 C atoms, and there will be an O atom inside the ring in between the C atoms. The product will be Benzene trizionide.
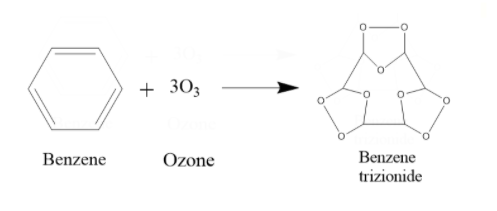
Next, the Benzene trizionide reacts with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$. It prevents further oxidation of the compound. What happens is, the molecule breaks off at the places where there is a carbon-oxygen-carbon bond. That O actually combines with water to form ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$. So, as that O is gone, the compound will split up into 3 fragments. Each of these fragmented compounds will have 2 C atoms, and both of them form double bonds with the O that they are bonded with. When treated with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$, 1 mole Benzene trizionide thus breaks up into 3 moles of glyoxal and 3 moles of ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$.
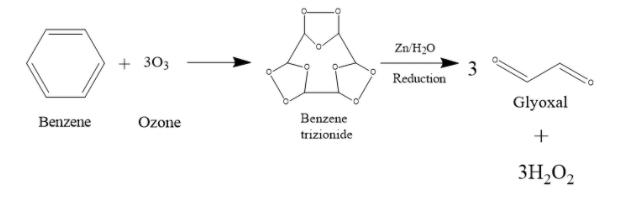
Therefore, the answer is option (B) 3 moles of glyoxal.
Note: Make sure that you balance the equations. Only then, do you get the correct answer. The correct structure of benzene trizionide is the one in the question. You might see many different structures of this everywhere. Make sure that the structure you use has satisfied octet configuration.
Complete step by step solution:
i) Ozonolysis is an organic reaction in which the oxidative cleavage of an unsaturated bond in a compound occurs when reacted with ozone. The end product will be an organic compound in which multiple carbon – carbon bonds have been replaced with bonds to oxygen.
ii) Here we have to find the end product for ozonolysis of benzene, followed by reaction with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$.
iii) Let us first see what the product will be after ozonolysis of benzene. During ozonolysis of benzene, what happens is an ozone is added to each pi bond of the benzene. Hence the product will be such that in the place of a double bond, there will be 2 O atoms attached as a chain outside the ring in between the 2 C atoms, and there will be an O atom inside the ring in between the C atoms. The product will be Benzene trizionide.

Next, the Benzene trizionide reacts with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$. It prevents further oxidation of the compound. What happens is, the molecule breaks off at the places where there is a carbon-oxygen-carbon bond. That O actually combines with water to form ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$. So, as that O is gone, the compound will split up into 3 fragments. Each of these fragmented compounds will have 2 C atoms, and both of them form double bonds with the O that they are bonded with. When treated with Zn + ${{H}_{2}}O$, 1 mole Benzene trizionide thus breaks up into 3 moles of glyoxal and 3 moles of ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$.

Therefore, the answer is option (B) 3 moles of glyoxal.
Note: Make sure that you balance the equations. Only then, do you get the correct answer. The correct structure of benzene trizionide is the one in the question. You might see many different structures of this everywhere. Make sure that the structure you use has satisfied octet configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




